Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by a bacterium called Treponema pallidum. It spreads primarily through sexual contact but can also be transmitted from an infected mother to her baby during pregnancy (congenital syphilis). If untreated, syphilis progresses through different stages and can cause severe health complications.
Types (Stages) of Syphilis
Primary Syphilis
- A painless sore (chancre) appears at the site of infection, such as the genitals, rectum, or mouth.
- The sore heals on its own, but the infection remains in the body.
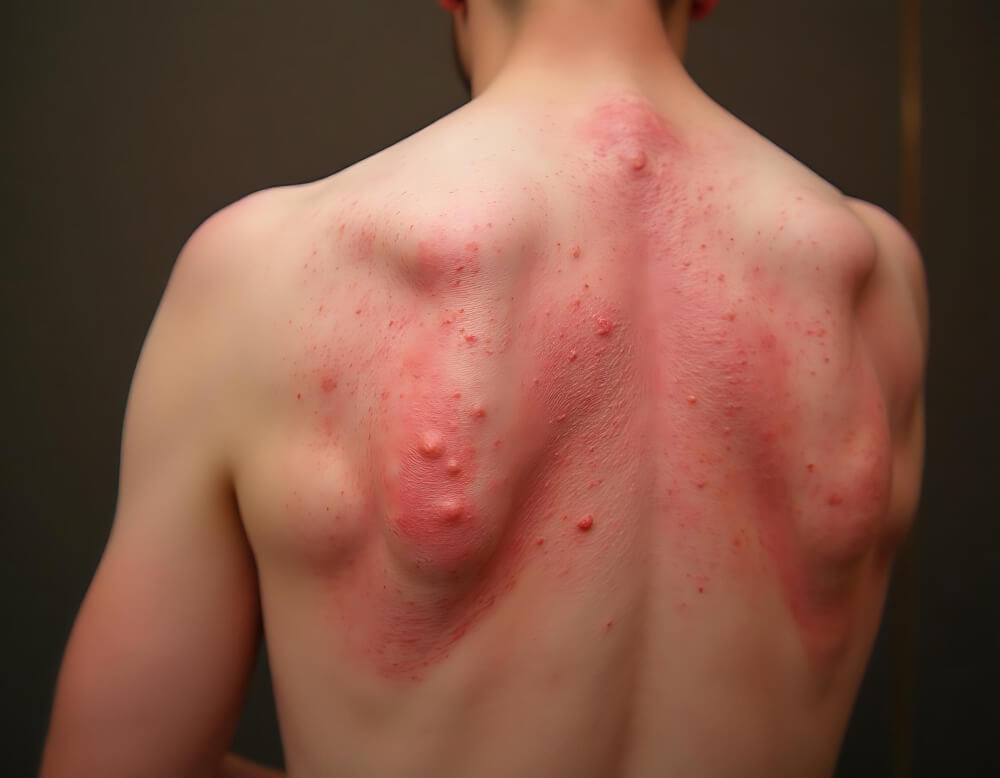
Secondary Syphilis
- Skin rashes, mucous membrane lesions, and flu-like symptoms appear weeks after the chancre heals.
- Symptoms may come and go over time.
Latent Syphilis
- A "hidden" stage with no visible symptoms.
- The infection can remain dormant for years, but it’s still active in the body.
Tertiary Syphilis
- Occurs years or decades after the initial infection if left untreated.
- Can damage the heart, brain, nerves, eyes, and other organs, leading to serious complications.
Congenital Syphilis
- Passed from an infected mother to her baby during pregnancy, leading to severe complications or stillbirth.
Causes of Syphilis
Mode of Transmission
- Unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected person.
- Direct contact with a syphilis sore or rash.
- From an infected mother to her baby during pregnancy or childbirth.
Risk Factors
- Having multiple sexual partners.
- Unprotected sex.
- Having another STI, such as HIV.
- Drug abuse or sharing needles.
Signs and Symptoms of Syphilis
Primary Stage
- A single, painless sore (chancre) at the site of infection (genitals, anus, or mouth).
- Swollen lymph nodes near the sore.
Secondary Stage
- Skin rashes (commonly on palms and soles).
- Fever and swollen lymph nodes.
- Sore throat, fatigue, and muscle aches.
- Hair loss in patches (alopecia).
- Mucous patches in the mouth or genitals.
Latent Stage
- No symptoms, but the infection is still present.
Tertiary Stage
- Neurological issues (headaches, numbness, and memory problems).
- Cardiovascular damage (aortic aneurysms).
- Blindness or deafness.
- Formation of gummas (soft, tumor-like growths on the body).
Congenital Syphilis
- Miscarriage or stillbirth.
- Bone deformities, rashes, and developmental delays in babies.
Complications of Untreated Syphilis
Neurological Damage
- Paralysis, dementia, or meningitis.
Cardiovascular Problems
- Damage to heart valves, arteries, and blood vessels.
Vision and Hearing Loss
- Blindness or deafness in advanced stages.
HIV Risk
- Increases the likelihood of contracting or spreading HIV.
Congenital Complications
- Severe birth defects or infant death.
Ayurvedic Perspective on Syphilis
In Ayurveda, syphilis can be correlated with Upadamsha, a disease described in ancient texts that is primarily linked to unclean or excessive sexual activities. It is considered a disorder of the Rakta Dhatu (blood tissue), involving an imbalance of the Doshas:
- Vata Dosha: Causes pain and neurological symptoms.
- Pitta Dosha: Leads to inflammation, rashes, and ulcers.
- Kapha Dosha: Results in glandular swelling and discharge.
- The accumulation of Ama (toxins) due to poor digestion and improper lifestyle further aggravates the condition.
Ayurvedic Treatment for Syphilis:
Panchakarma Therapy (Shodhana)
- Virechana (Purgation Therapy): Removes toxins from the blood and pacifies Pitta.
- Raktamokshana (Bloodletting): Purifies the blood and reduces inflammation.
- Abhyanga (Oil Massage):
- Swedana (Steam Therapy): Helps eliminate toxins through sweating.
- Virechana (Therapeutic Purgation) : Clears Pitta-related toxins from the system.
Dietary Recommendations
What to Eat:
- Light and easily digestible foods such as soups, porridges, and steamed vegetables.
- Bitter and astringent foods like neem leaves, bitter gourd, and fenugreek to purify the blood.
- Fresh fruits like pomegranate, amla (Indian gooseberry), and papaya to boost immunity.
- Herbal teas with tulsi (holy basil), turmeric, and ginger to reduce inflammation and enhance detoxification.
What to Avoid:
- Heavy, fried, oily, and spicy foods that aggravate Pitta and Kapha.
- Excess sugar, processed foods, and alcohol.
- Foods causing indigestion, such as dairy products, in some cases.
Lifestyle Recommendations
- Practice Safe Sex: Avoid multiple partners and use protection during intercourse.
- Maintain Hygiene: Wash affected areas regularly and wear clean clothes.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in yoga or light physical activities to boost circulation and immunity.
- Manage Stress: Practice pranayama (breathing exercises) and meditation to balance doshas.
Yoga Asanas
- Bhujangasana (Cobra Pose): Improves blood circulation.
- Paschimottanasana (Seated Forward Bend): Detoxifies the body.
- Vrikshasana (Tree Pose): Boosts immunity and calms the mind.
Pranayama
- Anulom Vilom (Alternate Nostril Breathing): Balances the doshas.
- Kapalabhati: Detoxifies the system and enhances blood purification.
Herbal Remedies
Neem (Azadirachta indica)
Purifies the blood and reduces infections.
Turmeric (Haridra)
Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial, aiding in wound healing.
Manjistha (Rubia cordifolia)
Cleanses the blood and pacifies Pitta and Kapha.
Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia)
Boosts immunity and detoxifies the system.
Triphala
A combination of three fruits to improve digestion and eliminate toxins.
Ashwagandha
Strengthens immunity and helps manage fatigue and neurological symptoms.
External Applications
- Apply neem paste or turmeric paste to any external sores or ulcers to promote healing.
- Use medicated oils like Jatyadi Taila to soothe inflammation and aid wound healing.
Ayurveda provides a holistic approach to managing syphilis by addressing the root causes, improving immunity, and detoxifying the body. By combining herbal remedies, panchakarma therapies, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle modifications, Ayurveda helps manage symptoms and supports overall health. However, for advanced stages or severe complications, seek immediate medical attention and combine Ayurvedic treatments with modern medical care.