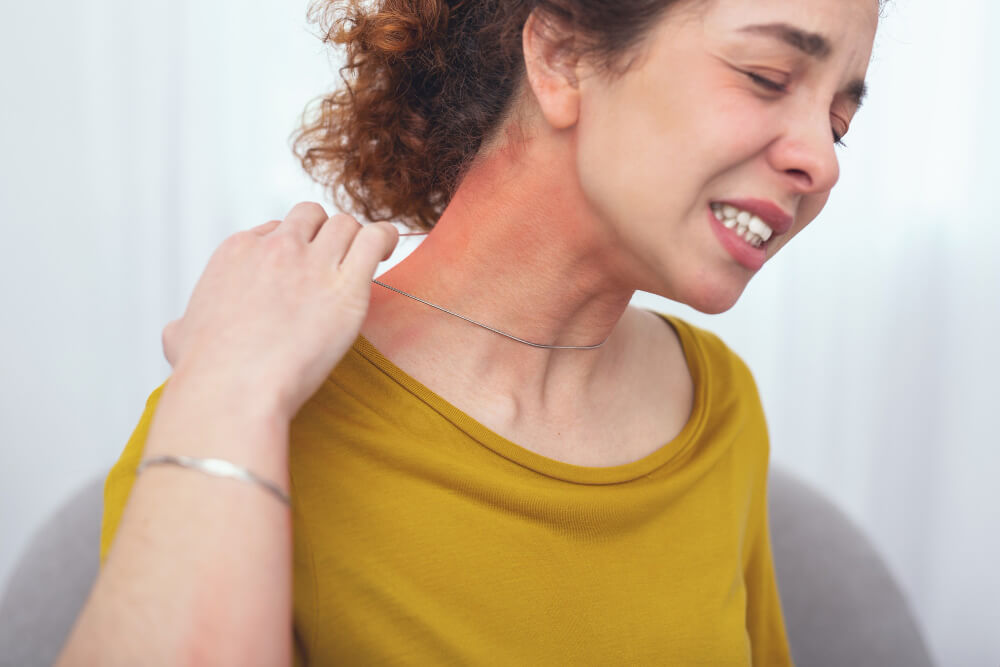
sialadenitis and sialadenosis
Sialadenitis is an infection or inflammation of the salivary glands, usually caused by a bacterial or viral infection. It most commonly affects the parotid or submandibular glands and can result in painful swelling, redness, and discomfort in the affected area.
Causes of Sialadenitis
- Bacterial Infection: Usually caused by Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus viridans, or Haemophilus influenzae, often due to reduced saliva flow.
- Viral Infection: Mumps virus can cause viral sialadenitis, particularly affecting the parotid glands.
- Dehydration or Poor Oral Hygiene: Reduced saliva flow encourages bacterial growth.
- Blockages: Salivary stones or strictures in the ducts can obstruct saliva flow and lead to infection.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like Sjogren’s syndrome can cause chronic inflammation of the glands.
Causes of Sialadenosis
- Metabolic Conditions: Diabetes, hypothyroidism, and liver disease can cause gland enlargement.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Deficiencies in vitamins or minerals, or eating disorders such as bulimia or anorexia.
- Medications: Certain drugs, like anti-hypertensives or psychotropic medications, can cause gland enlargement.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Changes in hormonal levels, especially in females, can lead to gland swelling.
Signs and Symptoms
Sialadenitis: (S/S)
- Pain and Swelling: Usually on one side of the face, near the affected gland.
- Redness and Tenderness: Skin over the gland becomes red and warm.
- Pus or Discharge: May drain from the duct into the mouth, with a foul taste.
- Dry Mouth and Difficulty Swallowing: Due to decreased saliva production.
- Fever and Malaise: May occur if the infection becomes systemic.
Sialadenosis: (S/S)
- Painless Swelling: Typically bilateral, affecting both sides of the face.
- Enlargement of the Gland: Noticeable increase in size, often in the parotid region.
- Dry Mouth: Mild dryness due to altered saliva composition.
- Minimal or No Pain: Distinguishing it from sialadenitis.
Complications of Sialadenitis and Sialadenosis
Sialadenitis Complications
- Abscess Formation: Severe cases may lead to pus-filled abscesses
- Chronic Infection: Repeated or untreated infections can cause long-term damage.
- Cellulitis: Infection may spread to surrounding tissues, causing serious complications
- Septicemia: Severe bacterial infections may enter the bloodstream.
Sialadenosis Complications
- Cosmetic Issues: Persistent gland enlargement can lead to facial asymmetry.
- Dysfunction of Salivary Glands: Long-term enlargement may impair normal salivary flow.
- Associated Metabolic Conditions: Worsening of underlying conditions like diabetes if untreated.
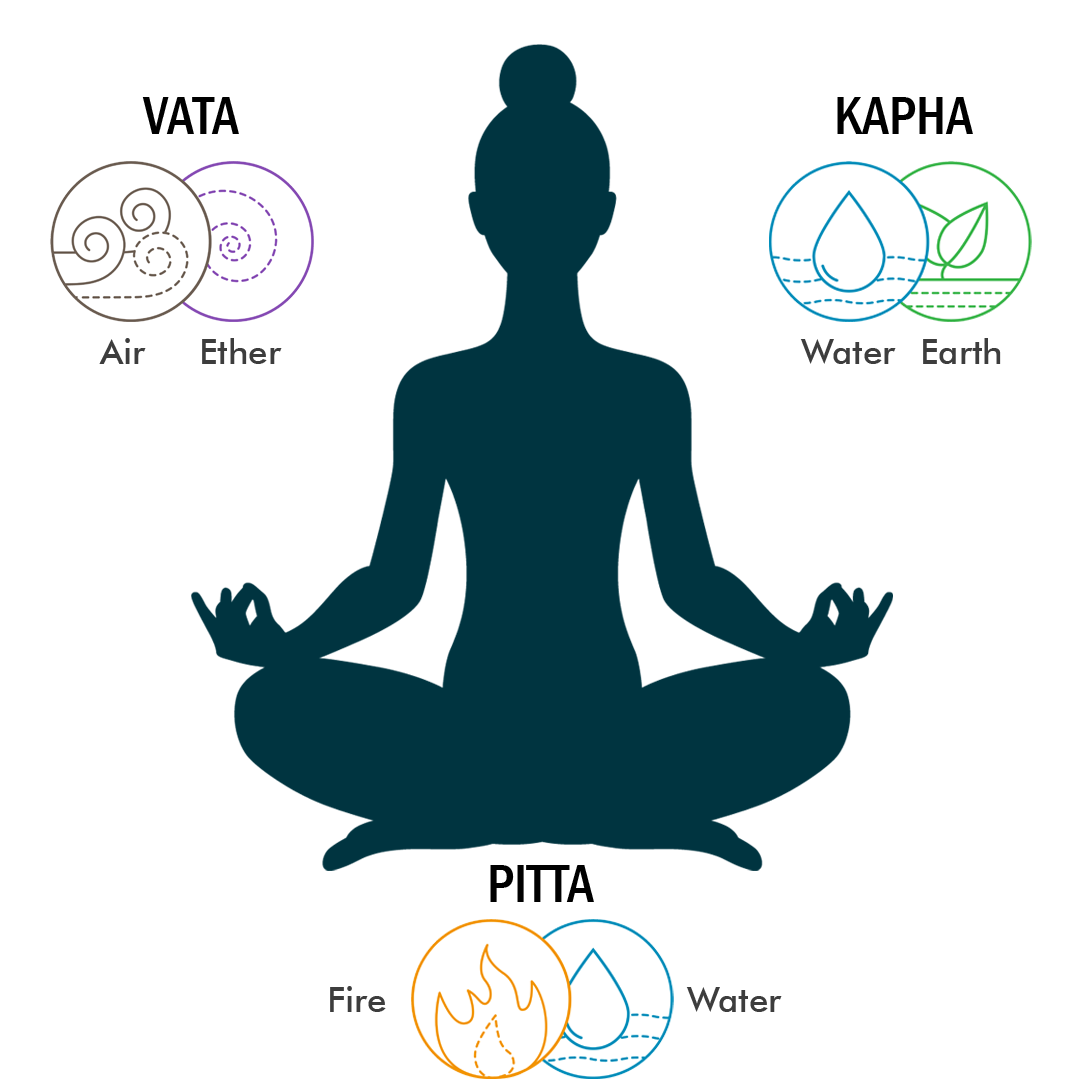
Ayurvedic Perspective on Sialadenitis and Sialadenosis
Sialadenitis (Mukhapaka and Upajihvika)
Ayurveda attributes sialadenitis to an imbalance of Pitta dosha and Kapha dosha, leading to inflammation and infection of the salivary glands. Ama (toxins) and poor oral hygiene contribute to this imbalance, causing blockage and infection. This condition can be associated with Mukhapaka (oral ulcers) and Upajihvika (affecting glands around the jaw and tongue).
Sialadenosis (Medo Vikara and Kapha Vikaras)
Sialadenosis is seen as a Kapha dosha imbalance, causing excess tissue growth and gland enlargement without inflammation. It is also associated with Medo Dhatu (fat tissue) abnormalities and improper metabolism. Hormonal imbalances, poor diet, and systemic conditions are recognized as contributing factors.
Ayurvedic Treatment for Sialadenitis and Sialadenosis
Detoxification and Purification (Shodhana)
- Virechana (Purgation Therapy): Cleanses excess Pitta dosha and toxins from the body.
- Nasya (Nasal Administration of Herbs): Using medicated oils like Anu Taila to reduce Kapha imbalance in the head and neck region.
External Therapies
- Kavala and Gandusha: Oil pulling or gargling with Sesame oil or Triphala decoction to cleanse the mouth and glands.
- Abhyanga (Oil Massage): Massaging the face and neck with Mahanarayana Taila or Ksheerabala Taila to improve circulation and reduce swelling.
Dietary Recommendations (Ahara)
- Pitta-Pacifying Diet: Include cooling foods like cucumber, coconut water, and ghee.
- Kapha-Reducing Diet: Reduce heavy, oily, and sweet foods; include warm, spicy, and light meals.
- Herbal Teas: Regular intake of teas made from ginger, turmeric, and cinnamon to improve digestion and immunity.
Lifestyle Recommendations (Vihara)
- Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing with herbal tooth powders containing neem and clove.
- Stress Management: Practice yoga and pranayama to balance hormones and reduce stress.
- Regular Exercise: Gentle exercise to improve metabolism and reduce gland enlargement.
Herbal Remedies
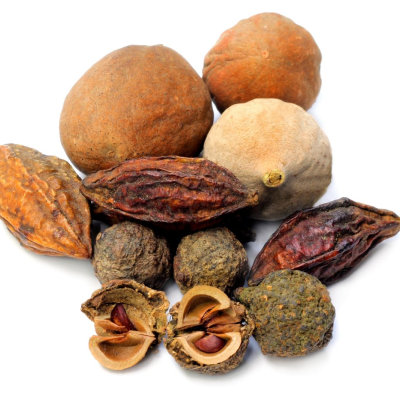
Triphala
Used as a mouthwash to reduce inflammation and improve oral hygiene.
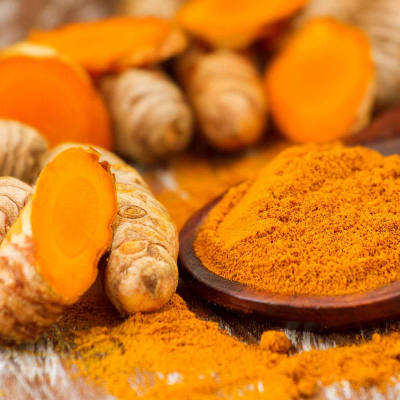
Turmeric (Haridra)
Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial; used internally and as a paste.
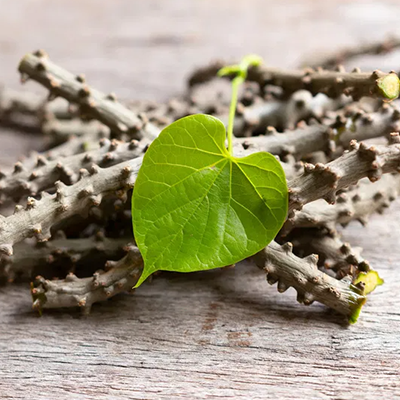
Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia)
Boosts immunity and detoxifies the system.
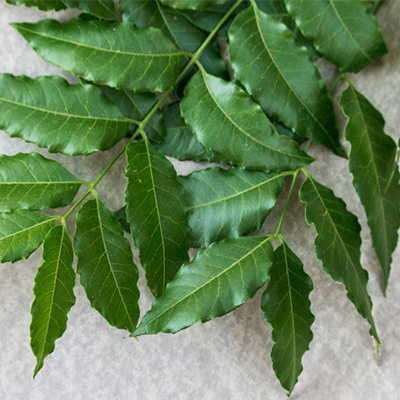
Neem (Nimba)
Has antibacterial properties for infection control.
Dashamoola Decoction
Helps reduce swelling and inflammation.
While sialadenitis and sialadenosis are distinct conditions affecting the salivary glands, both require a combination of proper oral hygiene, balanced diet, and herbal therapies in Ayurveda. An individualized approach that incorporates detoxification, rejuvenation, and lifestyle changes can effectively manage symptoms and support long-term health.
Know your body type