Reiter's Syndrome, also called Reactive Arthritis, is a type of inflammatory arthritis that occurs as a reaction to an infection in another part of the body, usually the urinary tract, intestines, or reproductive organs. It is called "reactive" because the immune system reacts to an infection, leading to inflammation in the joints, eyes, and urinary system.
Causes of Reactive Arthritis
Reactive Arthritis typically develops after a bacterial infection, especially in the following cases:
Infections of the Urinary Tract or Genitals
- Caused by bacteria like Chlamydia trachomatis.
Gastrointestinal Infections
- Foodborne bacteria like Salmonella, Shigella, Yersinia, and Campylobacter can trigger this condition.
Respiratory Infections
- Some respiratory tract infections can also cause reactive arthritis.
Who is at Risk?
- It is more common in men between the ages of 20–40.
- People with a genetic predisposition (HLA-B27 gene) are more likely to develop the condition.
Signs and Symptoms of Reactive Arthritis
Reactive Arthritis often involves a triad of symptoms:
Arthritis (Joint Inflammation)
- Pain, swelling, and stiffness in large joints such as the knees, ankles, and feet.
- Symptoms may occur asymmetrically (not the same on both sides of the body)
Eye Inflammation (Conjunctivitis or Uveitis)
- Red, painful, and irritated eyes.
- Blurred vision or light sensitivity.
Urinary Symptoms
- Burning sensation during urination (urethritis).
- Increased frequency of urination.
Other symptoms include
- Swelling in fingers or toes (sausage-like appearance).
- Heel pain (due to inflammation of tendons).
- Skin rashes or sores, particularly on the palms, soles, or mouth.
- Back pain or stiffness in some cases.
Ayurvedic Perspective of Reactive Arthritis
In Ayurveda, Reactive Arthritis can be compared to "Ama Vata" or "Sandhigata Vata". It is caused due to an imbalance of Vata dosha and accumulation of Ama (toxins) in the joints, leading to pain and inflammation.
- Vata Dosha: Governs movement and lubrication of joints. An aggravated Vata causes dryness, stiffness, and pain in the joints.
- Ama: Undigested food or toxins accumulate due to poor digestion (Agni imbalance). Ama circulates in the body and gets deposited in the joints, triggering inflammation.
Ayurvedic Treatment for Reactive Arthritis
Ayurveda focuses on balancing the doshas, detoxifying the body, and improving digestion to remove Ama.
Detoxification (Panchakarma Therapy)
- Panchakarma procedures help remove accumulated toxins and purify the body:
- Virechana (Therapeutic Purgation): Removes excess Pitta and toxins.
- Basti (Enema Therapy): Herbal decoctions and oils help pacify Vata dosha and lubricate joints.
- Abhyanga (Oil Massage): Warm medicated oils like Mahanarayana Taila or Dashmool Taila are used to reduce stiffness and pain.
Diet and Lifestyle Changes
Diet to Remove Ama
- Eat easily digestible foods like khichdi, cooked vegetables, and soups.
- Avoid cold, oily, and processed foods that increase Ama.
- Include spices like ginger, turmeric, cumin, and ajwain in meals to improve digestion.
Stay Hydrated
- Drink warm water throughout the day to flush out toxins.
Avoid Heavy Exercise
- Gentle yoga and stretching help reduce stiffness without aggravating Vata dosha.
Sleep and Stress Management
- Maintain a balanced sleep schedule and practice meditation or pranayama to reduce stress.
External Therapies
Potli Massage (Pinda Sweda)
- Massage using herbal poultices to reduce joint pain and inflammation.
Hot Fomentation
- Applying heat to painful joints relieves stiffness.
Herbal Remedies
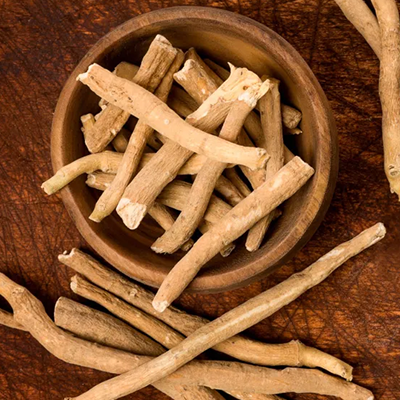
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera)
- Reduces inflammation, strengthens joints, and pacifies Vata.
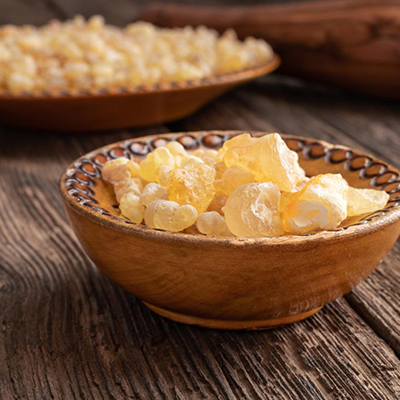
- Guggulu (Commiphora mukul):
- Known for its anti-inflammatory properties. Yograj Guggulu and Mahavishgarbha Taila are beneficial.
Shallaki (Boswellia serrata)
Improves joint health and reduces swelling.
Triphala
Detoxifies the body and improves digestion, preventing Ama accumulation.
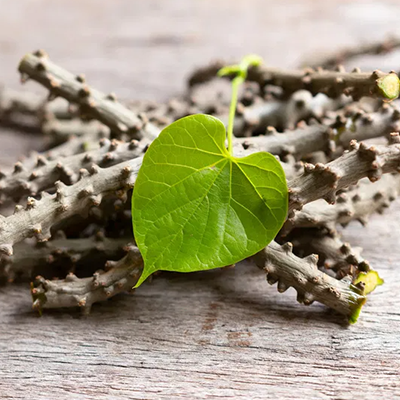
Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia)
Boosts immunity and reduces inflammation.
Reactive Arthritis, or Reiter's Syndrome, is an inflammatory condition triggered by an infection. Ayurveda treats this by addressing the root cause—removing toxins (Ama), balancing Vata dosha, and strengthening digestion. Through Panchakarma, herbal medicines, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle changes, the inflammation can be managed effectively. A holistic Ayurvedic approach not only alleviates symptoms but also restores long-term joint health and immunity.