- +033 2572 7171
- info@dhanvantary.com

4.5 Rating | 4500 Review

4.5 Rating | 4500 Review
Vitamin B6, also known as Pyridoxine, is a water-soluble vitamin. It plays a crucial role in the synthesis of serotonin and norepinephrine, which function as neurotransmitters that convey signals to the brain. Additionally, it is essential for the production of myelin, a protein sheath that encases nerve cells.
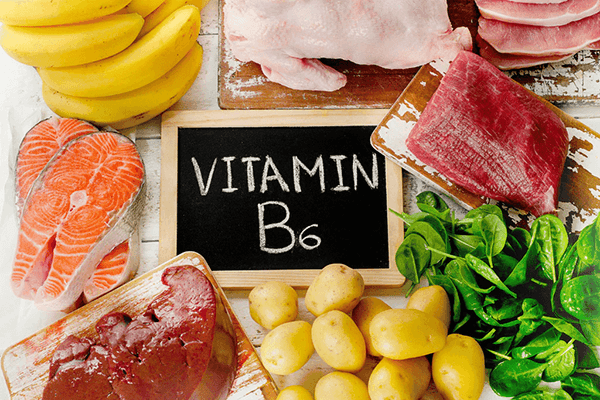
Vitamin B6 deficiency can lead to various health issues, including:
Maintaining health offers numerous benefits, which are outlined below:
Vitamin B6 is essential for the synthesis of heme, a critical component of hemoglobin. The primary sites for hemoglobin production in the body are the bone marrow and liver. A deficiency in vitamin B6 can lead to a specific type of anemia known as Sideroblastic anemia.
This vitamin plays a vital role in the metabolic processes within the body. It is necessary for the enzymatic breakdown of carbohydrates, as it facilitates the release of glycogen from storage cells.
Vitamin B6 is crucial for the synthesis of neurotransmitters, including GABA, dopamine, and serotonin. A lack of this vitamin may contribute to the onset of depression.
Vitamin B6 supports optimal liver function by aiding in the removal of toxins. Insufficient levels of this vitamin can result in liver dysfunction.
This vitamin is important for maintaining normal nerve function and regulating blood sugar levels.
Vitamin B6 is generally considered safe; however, the potential for complications may arise depending on the dosage consumed. The following effects may occur with high doses of Vitamin B6:
Conversely, a deficiency in Vitamin B6 may lead to:
The recommended dosage varies based on age and sex, as detailed below:
