- +033 2572 7171
- info@dhanvantary.com

4.5 Rating | 4500 Review

4.5 Rating | 4500 Review
Valine is classified as a branched-chain amino acid and shares structural and functional similarities with leucine and isoleucine. Collectively, these three branched-chain amino acids account for approximately 70 percent of the amino acids present in the human body. Characteristically hydrophobic, they are predominantly located within the interior of proteins.
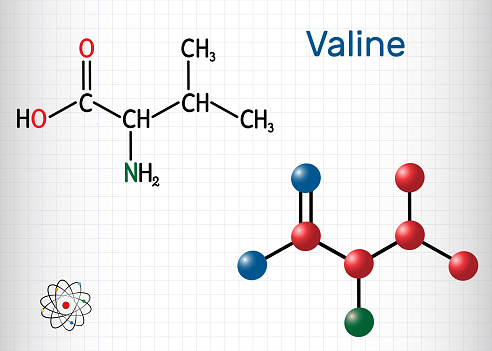
The discovery of valine dates back to 1901, attributed to the German scientist Emil Fischer. As one of the essential amino acids, valine cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through dietary sources, including various plant and animal products. It is found in high concentrations within muscle tissues. The formation of binding and recognition sites on cells is contingent upon the presence of valine; without it, the translation of chemical signals from the brain is hindered. Additionally, valine plays a crucial role in maintaining both the structural and functional integrity of the human body.
Animal sources: Valine is abundantly found in animal products such as meat, poultry, and fish. Dairy items, including milk, cheese, and yogurt, are also rich in valine.
Plant sources: Plant-based sources of valine include peanuts, legumes, beans, lentils, soy, mushrooms, sesame seeds, spinach, and kale, all of which contain substantial amounts of this amino acid.
A deficiency in valine can lead to Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD), a condition characterized by impaired metabolism of valine, leucine, and isoleucine. This disorder is named for the distinctive maple syrup-like odor of the urine in affected individuals. Additionally, complications arising from valine deficiency may impact the myelin sheath surrounding the nerves.
Risk of Higher Intake of Valine
An excessive intake of valine may lead to symptoms such as hallucinations and a sensation of skin crawling. Overconsumption can result in the accumulation of ammonia in the body, which may disrupt the normal functioning of the kidneys and liver.
