- +033 2572 7171
- info@dhanvantary.com

4.5 Rating | 4500 Review

4.5 Rating | 4500 Review
Protein plays a vital role in maintaining overall health within the body. They are among the most prevalent types of molecules found in humans. Proteins serve as major components of our biological structure, with the highest concentrations located in the skin, hair, muscles, and various organs. They contribute to the strength of these structures and facilitate numerous bodily movements, including muscle contractions and the transportation of food through the digestive system.
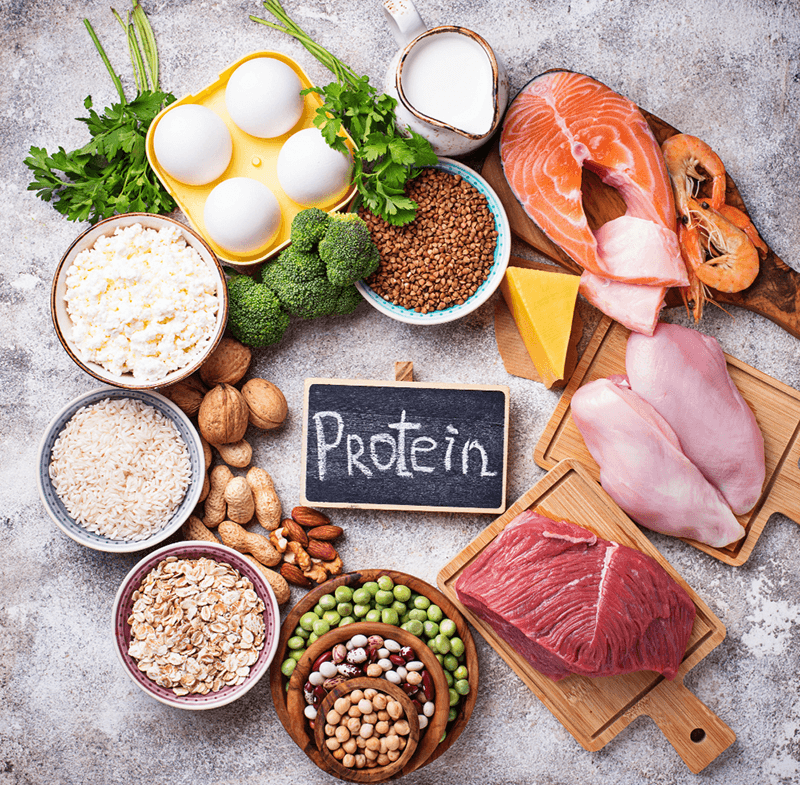
Proteins are essential for performing various critical functions, providing structural integrity and strength to cells and tissues. They regulate numerous biochemical reactions and support the immune system's health. Additionally, proteins are involved in cell division and aid in the repair of damaged cells, ensuring a continuous supply of healthy cells.
Proteins can range from simple chains of fewer than 100 amino acids to complex structures composed of multiple chains. These structural proteins provide shape and support to cells, connective tissues, and organs.
Actin and myosin are two filamentous proteins found in muscles that facilitate muscle contraction.
Antibodies, which are proteins, assist the body in combating various infections, thereby promoting a robust immune system.
With thousands of biochemical reactions occurring daily, the body requires energy to facilitate these processes. Proteins function as enzymes, enhancing these biochemical reactions.
Proteins are responsible for transporting other proteins and compounds throughout the body. Hemoglobin, a transport protein found in red blood cells, carries oxygen from the lungs to tissues and returns carbon dioxide to the lungs for elimination.
Protein are the building elements of our body, so the deficiency of Protein in the body leads to health impairment.
High protein consumption can lead to various adverse effects, including weight gain, osteoporosis, kidney issues, and multiple nutritional deficiencies. An excessive intake of protein results in the accumulation of amino acids (hyperaminoacidemia) and elevated levels of ammonia (hyperammonemia) in the body. These conditions pose significant health risks and may contribute to premature mortality.
