- +033 2572 7171
- info@dhanvantary.com

4.5 Rating | 4500 Review

4.5 Rating | 4500 Review
Magnesium is essential for the production of ATP within the human body. It serves as a cofactor for various enzymes and is believed to regulate over 300 biochemical reactions. Classified as a macromineral, magnesium is required in larger quantities compared to trace elements. It is recognized as the second most abundant element found in human cells, where it facilitates numerous cellular functions. Among its various forms, magnesium chloride is the most readily available and easily absorbed.
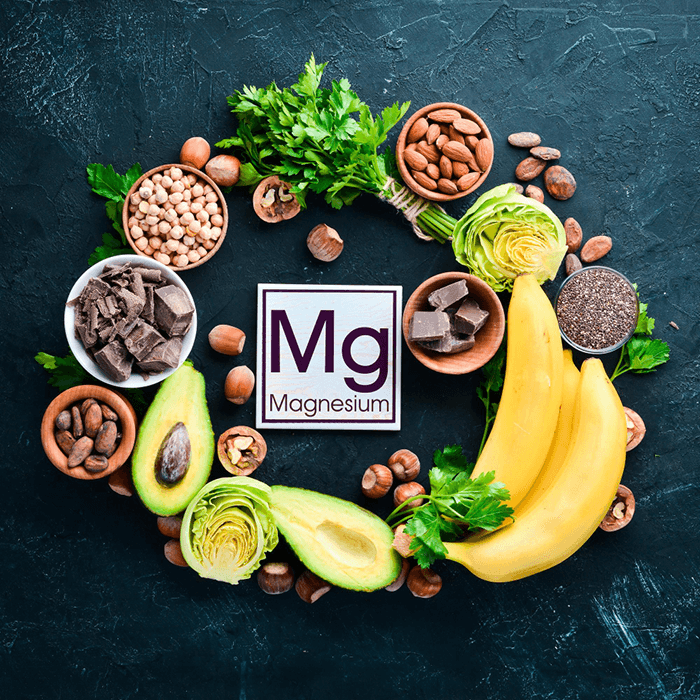
Magnesium is crucial for bone formation, aiding in the incorporation of calcium into the skeletal structure. Adequate magnesium intake enhances bone density and lowers the risk of osteoporosis, particularly in women. It also plays a role in activating vitamin D.
Magnesium is involved in carbohydrate and glucose metabolism, improving insulin secretion and proving beneficial for individuals with diabetes.
It helps maintain healthy lipid levels in the body, thereby supporting cardiovascular health.
Magnesium alleviates symptoms associated with premenstrual syndrome, including insomnia, bloating, leg swelling, breast tenderness, and weight gain.
It contributes to the maintenance of a healthy balance of minerals such as calcium, sodium, and potassium.
Excessive magnesium consumption can lead to various health complications. An overdose may result in kidney damage and impair the central nervous system, potentially causing paralysis. Additionally, high magnesium intake can lead to diarrhea, which may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and abdominal cramps.
As already discussed magnesium is an important mineral for the several body functions.
Deficiency of magnesium results in the various health issues which are given below:-
Green leafy vegetables such as spinach, legumes, and broccoli serve as excellent sources of magnesium. Additionally, whole grains, brown rice, black beans, oatmeal, carrots, bananas, milk, avocados, cereals, peanuts, almonds, and both soymilk and yogurt provide substantial amounts of this essential mineral.
