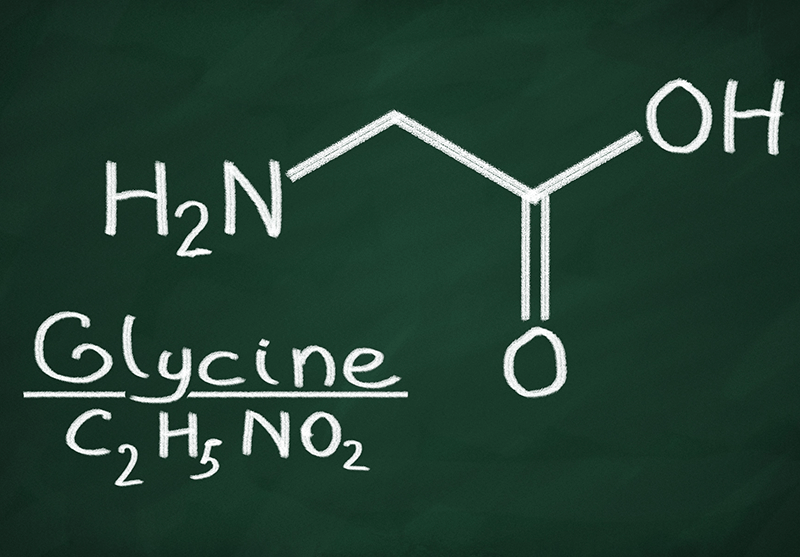
Glycine is recognized as the simplest amino acid and is essential for the biosynthesis of nucleic acids, bile acids, porphyrins, phosphates, and other amino acids. It ranks as the second most prevalent amino acid in proteins. Additionally, glycine is a component of the coenzyme glutathione, which plays a crucial role in various biochemical reactions. The health benefits of glycine are numerous and are elaborated upon below.
Health Benefits of Glycine
- Glycine is vital for the proper functioning of the nervous system and brain, acting as an inhibitory neurotransmitter that aids in the prevention of epileptic seizures.
- It is utilized in the management of hyperactivity and manic depression.
- Glycine participates in the biochemical processes that generate energy within the body.
- It contributes to the normal functioning of the prostate by facilitating the production of prostate fluid in men.
- Glycine promotes healthy nervous system operations.
- It plays a role in the synthesis of growth hormone.
- Glycine assists in regulating blood sugar levels, thereby reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- It aids in diminishing allergic and autoimmune responses.
- Glycine is beneficial for cognitive health and helps manage symptoms associated with schizophrenia, seizures, and other mental disorders.
- It supports the development of lean muscle mass.
- Glycine contributes to the maintenance of the gastrointestinal tract lining.
- It is effective in alleviating joint pain.
- Glycine can assist in weight loss efforts.
- It promotes kidney health.
- Glycine is advantageous for managing anxiety and depression.
- It may lower the risk of certain cancers.
- Glycine offers protection to the skin against signs of aging and cellular mutations.
- It is beneficial for enhancing sleep quality.
- Glycine plays a role in the production of red blood cells.
- It supports cardiovascular health and aids in lowering high blood pressure levels.
Glycine Sources
Glycine is present in various plant and animal sources, which include the following:
- Animal sources: Meat and fish.
- Dairy sources: Milk, cheese, and yogurt.
- Plant sources: Pumpkin, beans, soybeans, spinach, kale, legumes, cabbage, cauliflower, cucumber, bananas, and kiwis.
Glycine Deficiencies
Deficiencies in glycine are generally rare. However, they may occur in individuals who are malnourished or those suffering from conditions such as cancer or AIDS. Individuals with digestive disorders may experience low energy levels and fatigue due to inadequate glycine levels.
Recommended Daily Intake of Glycine
The minimum effective dose of glycine supplementation for humans typically ranges from 1 to 2 grams. However, doses as high as 45 grams have been administered without any adverse effects reported.
Potential Side Effects of Glycine
The consumption of glycine may lead to side effects such as nausea, vomiting, mild dizziness, and minor digestive issues.
Additional side effects may arise when glycine is taken in conjunction with medications for schizophrenia. In such cases, symptoms may include skin rashes, wheezing, itching, swelling of the mouth, and difficulties in swallowing and breathing.