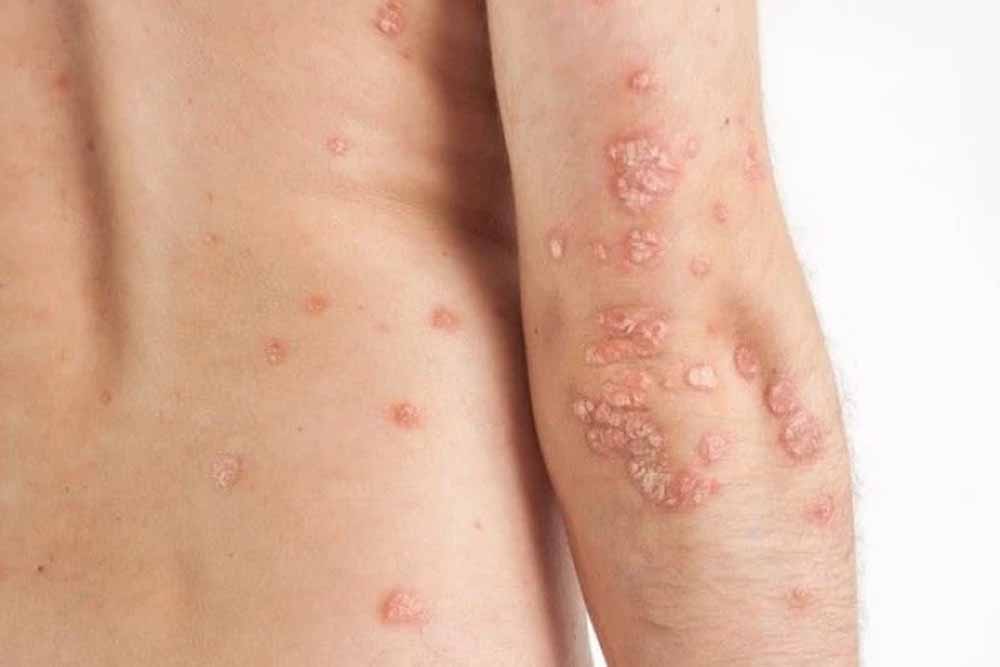
Neurodermatitis, also known as Lichen Simplex Chronicus, is a chronic skin condition characterized by intense itching and scratching, leading to thickened, leathery, and discoloured skin. It often begins with a localized itch that becomes worse with repeated scratching, creating a vicious cycle.
Body Parts Affected by Neurodermatitis
Neurodermatitis can occur on any part of the body but is most commonly seen on:
- Scalp
- Neck
- Shoulders
- Wrists
- Forearms
- Ankles
- Upper thighs
- Genital and anal areas
Causes of Neuro-dermatitis
The exact cause of neuro-dermatitis is unknown, but certain factors contribute to its development:
1. Stress and Anxiety:
- Emotional stress often triggers or exacerbates itching.
2. Skin Irritants:
- Tight clothing, rough fabrics, or chemical exposure can irritate the skin.
3. Underlying Skin Conditions:
- Associated with eczema, psoriasis, or dry skin conditions.
4. Neurological Factors:
- Nerve damage or disorders that cause itching (e.g., diabetic neuropathy).
5. Allergic Reactions:
- Allergies to specific foods or substances can worsen symptoms.
6. Infections or Injuries:
- Minor cuts or infections may trigger localized itching, leading to neuro-dermatitis.
7. Habitual Scratching:
- Persistent scratching reinforces the condition, even in the absence of an underlying cause.
Symptoms of Neuro-dermatitis
- Intense itching in a specific area (may worsen at night or during stress).
- Thickened, rough, and scaly patches of skin.
- Discoloration (skin may appear darker or lighter in affected areas).
- Pain, soreness, or burning sensation due to excessive scratching.
- Skin infections from open wounds caused by scratching.
Pathology of Neuro-dermatitis
1. Cycle of Itch and Scratch:
- The condition starts with an itch, causing the individual to scratch. The repeated scratching thickens the skin, making it more sensitive and itchier over time.
2. Skin Thickening:
- Chronic mechanical trauma due to scratching leads to lichenification (thickened and leathery skin).
3. Inflammation:
- Persistent scratching induces localized skin inflammation. Immune cells infiltrate the area, leading to redness and swelling.
4. Nerve Sensitization:
- Over time, nerve endings in the skin become hypersensitive, perpetuating the itch-scratch cycle.
Types of Neuro-dermatitis
1. Localized Neuro-dermatitis:
- Affects specific areas such as the scalp, neck, or genital region.
2. Generalized Neuro-dermatitis:
- Affects multiple areas of the body simultaneously, often associated with severe stress or systemic factors.
Ayurvedic Perspective of Neurodermatitis
In Ayurveda, neuro-dermatitis can be correlated with Kustha Roga (skin disorders) or Vicharchika (a type of eczema) caused by imbalances in the Pitta and Kapha doshas, along with the accumulation of Ama (toxins).
- Pitta Dosha: Causes burning sensation, redness, and inflammation.
- Kapha Dosha: Leads to thickened, rough skin and itchiness.
Ayurvedic Treatment for Neurodermatitis
Internal Cleansing (Shodhana):
Virechana (Purgation):
- Removes excess Pitta and toxins from the body.
- Herbs: Triphala Churna, Avipattikar Churna.
Raktamokshana (Bloodletting):
- Effective for chronic conditions with severe itching.
External Therapies (Bahya Chikitsa):
Application of Herbal Pastes (Lepa):
Chandanadi Lepa or Neem paste for soothing the skin.
Oil Massage (Abhyanga):
- Use medicated oils like Eladi Taila or Kumkumadi Taila to moisturize and heal the skin.
Bathing with Herbal Decoctions:
- Add Neem, Triphala, or Khadira decoctions to bathwater.
Herbal Remedies:
1. Neem (Azadirachta indica):
- Purifies the blood and reduces inflammation.
- Consume neem capsules or decoction.
2. Khadira (Acacia catechu):
- Treats skin disorders and reduces itching.
- Use as a decoction or in herbal formulations.
3. Manjistha (Rubia cordifolia):
- Supports detoxification and improves skin complexion.
4. Haridra (Curcuma longa):
- Anti-inflammatory and soothing properties.
- Mix turmeric with warm milk or honey.
5. Guggulu (Commiphora wightii):
- Helps in reducing inflammation and balancing doshas.
Ayurvedic Formulations:
- Mahamanjishtadi Kwath: Blood purifier.
- Khadirarishta: Treats skin disorders.
- Panchatikta Ghrita Guggulu: Balances doshas and heals chronic skin issues.
Diet:
- Avoid spicy, sour, and fried foods.
- Include fresh fruits, vegetables, and bitter herbs like neem and karela (bitter gourd).
- Drink warm water infused with turmeric or ginger.
Lifestyle:
- Avoid scratching or rubbing affected areas.
- Practice stress-relieving techniques like Pranayama and meditation.