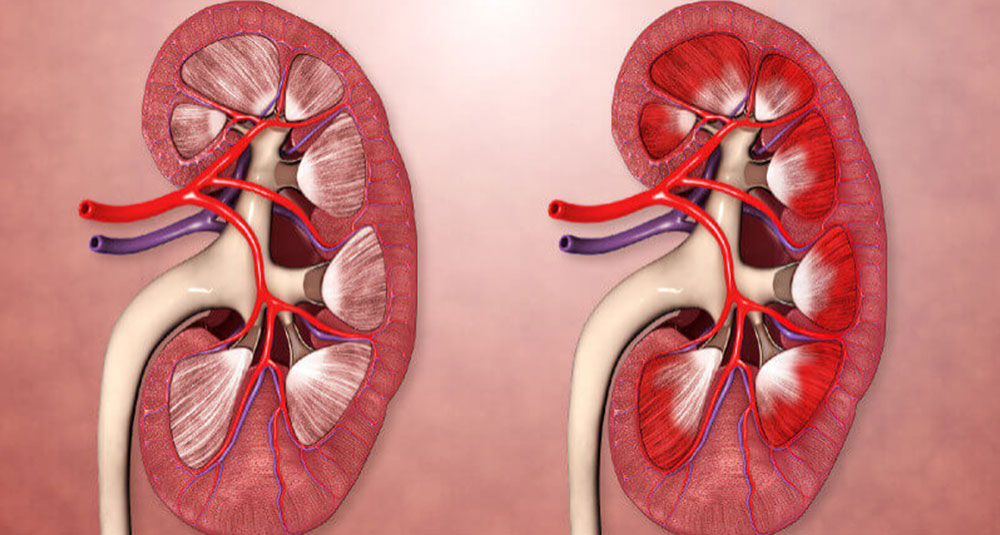
Membranous Glomerulonephritis
Membranous Glomerulonephritis also known as Membranous Nephropathy, is a kidney disorder caused by the thickening of the glomerular basement membrane in the kidneys. This thickening is usually due to immune complex deposits, which interfere with the kidney's ability to filter waste and excess fluid effectively.
Key Characteristics
- Gradual onset of nephrotic syndrome (proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, edema, and hyperlipidemia).
- Can lead to chronic kidney disease or kidney failure if untreated.
Causes of Membranous Glomerulonephritis
1. Primary (Idiopathic):
- No identifiable underlying cause.
- Often linked to autoantibodies targeting specific proteins in the kidney (e.g., phospholipase A2 receptor).
2. Secondary:
- Caused by underlying conditions such as:
- Infections (e.g., Hepatitis B, C, or syphilis)
- Autoimmune diseases (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus)
- Cancers (e.g., lung, colon, or breast cancer)
- Certain medications (e.g., NSAIDs or gold therapy)
Symptoms
- Proteinuria (foamy urine due to excess protein)
- Swelling (oedema), particularly in the legs, ankles, and around the eyes
- High blood pressure
- Increased cholesterol and triglycerides
- Fatigue and weakness
- Increased risk of infections and blood clots
Key diagnostic tests include
- Urine Tests: Proteinuria and hematuria detection.
- Blood Tests: Hypoalbuminemia, elevated creatinine, lipid abnormalities, and antibody tests.
- Kidney Biopsy: Definitive diagnosis through histological examination.
- Imaging Studies: Renal ultrasound or CT/MRI.
- Screening for Secondary Causes: Infection, cancer, or autoimmune disorders.
Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for determining the appropriate treatment and preventing complications such as kidney failure.
Ayurvedic Treatment for Membranous Glomerulonephritis
Panchakarma Therapies
- Virechana (Purgation Therapy): Helps remove accumulated toxins and balance Pitta.
- Basti (Medicated Enema): Strengthens kidney function and clears urinary channels.
Dietary Recommendations
Foods to Include:
- Fresh fruits like pomegranate and watermelon (in moderation).
- Vegetables such as bottle gourd, ridge gourd, and spinach.
- Easily digestible grains like rice and barley.
Foods to Avoid:
- Salty, spicy, and processed foods.
- Heavy and oily foods that aggravate Kapha and Ama.
Lifestyle recommendations
- Stay hydrated but avoid over hydration to prevent additional kidney strain.
- Avoid suppressing natural urges like urination.
- Engage in light physical activities like yoga and pranayama (e.g., Anulom Vilom).
Herbal Remedies
Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa):
Reduces swelling and supports kidney function.
Gokshura (Tribulus terrestris):
Promotes urinary health and detoxification.
Varuna (Crataeva nurvala):
Helps in clearing blockages in urinary channels.
Kaasni (Cichorium intybus):
Protects kidney tissues and reduces inflammation.
Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia):
Boosts immunity and reduces toxin accumulation.
Manjistha (Rubia cordifolia):
Acts as a blood purifier and anti-inflammatory.
Preventive Measures in Ayurveda
- Regular detoxification through Panchakarma.
- Consumption of immunity-boosting herbs like Amalaki (Indian Gooseberry).
- Avoidance of factors that aggravate doshas (e.g., excessive salt, dehydration).
Ayurvedic treatment offers a holistic approach to managing Membranous Glomerulonephritis by addressing the root cause, improving kidney function, and supporting overall health. It should be undertaken under the supervision of an experienced Ayurvedic practitioner.
Know your body type