Leukaemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, where blood cells are produced. It involves the abnormal production of white blood cells (WBCs), which play a crucial role in fighting infections. These abnormal cells multiply uncontrollably, crowding out normal blood cells, and impair the body's ability to function effectively.
Types of Leukemia
There are four primary types of leukemia:
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): Common in children but can occur in adults.
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): Mostly affects adults but can also occur in children.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Often seen in adults over 55 years.
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): Common in adults and progresses slowly over time.
Causes of Leukemia
The exact cause of leukemia is often unknown, but various factors may contribute:
1. Genetic Factors:
- Mutations in DNA that control blood cell production.
- Genetic disorders like Down syndrome.
2. Environmental Factors:
- Exposure to high levels of radiation.
- Long-term exposure to chemicals like benzene.
3. Lifestyle Factors:
- Smoking increases the risk of AML.
4. Immune System Problems:
- Weakened immunity can fail to detect abnormal cells.
5. Family History:
- A family history of leukemia slightly increases the risk.
Symptoms of Leukemia
The symptoms vary depending on the type and stage of leukemia but may include:
1. General Symptoms:
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Fever and night sweats.
- Unexplained weight loss.
2. Hematologic Symptoms:
- Frequent infections due to a lack of healthy WBCs.
- Easy bruising and bleeding, including nosebleeds or gum bleeding.
- Anaemia symptoms like pale skin and breathlessness.
3. Other Symptoms:
- Swollen lymph nodes.
- Enlarged spleen or liver (causing abdominal discomfort).
- Bone or joint pain.
Complications of Leukemia
- Infections: Impaired immunity increases vulnerability to infections.
- Anaemia: Insufficient production of red blood cells.
- Bleeding Disorders: Platelet deficiency causes excessive bleeding.
- Organ Damage: The build-up of leukaemia cells in the liver, spleen, or brain.
- Treatment-Related Complications: Side effects of chemotherapy or radiation, such as organ toxicity and secondary cancers.
In Ayurveda, leukemia can be related to Rakta Dhatu Dushti (vitiation of blood tissue) and imbalance of Tridoshas—Vata, Pitta, and Kapha. It is primarily associated with aggravated Pitta (fire element) causing excessive heat and metabolic dysfunction, leading to abnormal blood production.
Ayurvedic Terms for Leukemia
- Raktapitta: Hemorrhagic disorders.
- Arbuda: Tumorous growths.
- Panduroga: Anemia-like symptoms.
Ayurvedic Treatment for Leukemia
Ayurvedic treatment focuses on detoxifying the body, balancing doshas, and rejuvenating tissues:
Detoxification (Shodhana):
- Virechana (Purgation): Removes toxins and balances Pitta.
- Raktamokshana (Bloodletting): Purifies the blood.
Dietary Recommendations:
- Avoid spicy, fried, and processed foods.
- Consume fresh fruits like pomegranate and vegetables such as bitter gourd.
- Include herbal teas made from tulsi (holy basil) and ginger.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Practice yoga and meditation to reduce stress.
- Ensure adequate sleep and avoid overexertion.
Rasayana Therapy (Rejuvenation):
- Use of rejuvenating formulations like Chyawanprash to strengthen immunity.
Panchakarma Therapy: Aimed at holistic detoxification and balancing doshas.
Herbal Remedies
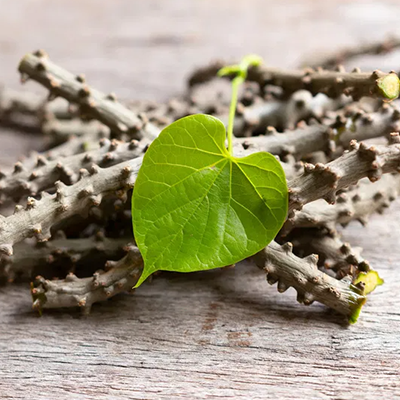
Manjistha (Rubia cordifolia):
Purifies and detoxifies the blood.
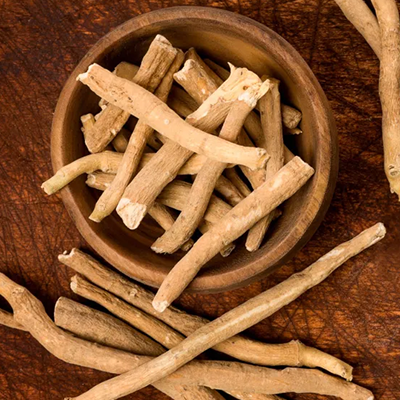
Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia):
Boosts immunity and balances Tridoshas.
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera):
Acts as a natural adaptogen and strengthens the body.
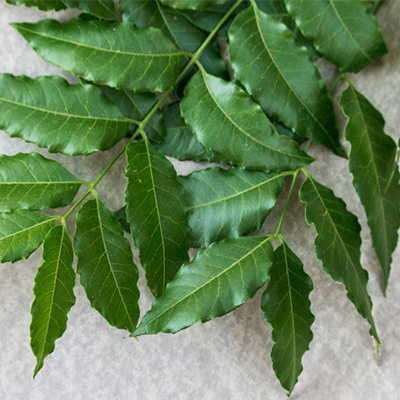
Neem (Azadirachta indica):
Reduces infections and purifies blood.
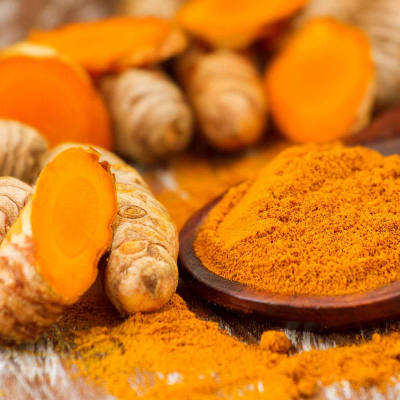
Turmeric (Curcuma longa):
Anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties.
While Ayurveda can support immune function, detoxification, and symptom relief, leukemia requires conventional medical interventions like chemotherapy, radiation, or bone marrow transplantation. Ayurveda can complement these treatments by reducing side effects, improving quality of life, and supporting long-term recovery.
Consultation with an experienced Ayurvedic practitioner and oncologist is essential for an integrative treatment approach.