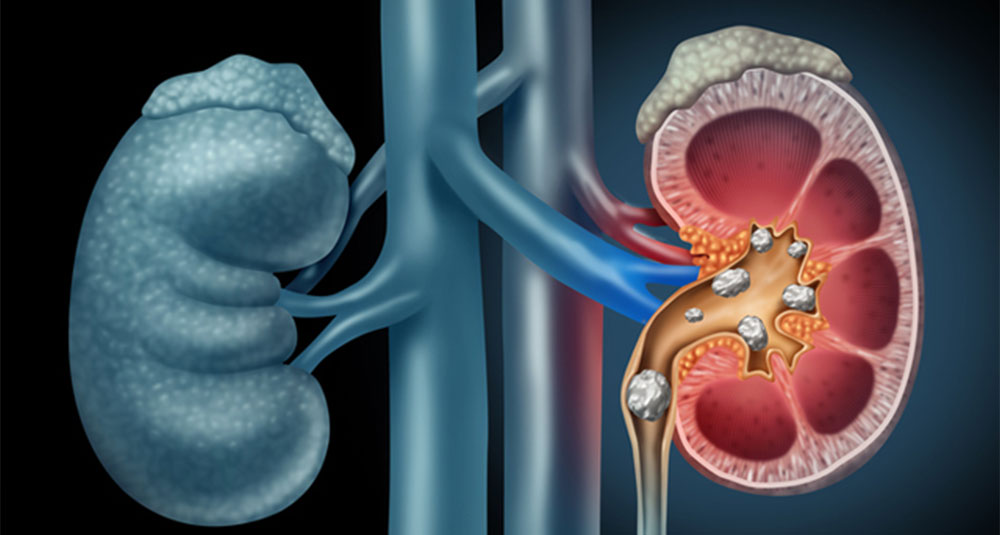
Kidney stones (renal calculi or nephrolithiasis) are solid masses formed from crystals in the kidneys. They develop when minerals and salts, such as calcium, oxalate, and uric acid, become concentrated in the urine.
Causes
- Dehydration: Insufficient water intake concentrates minerals in urine.
- Diet: High intake of salt, protein, and oxalate-rich foods.
- Medical Conditions: Hyperparathyroidism, gout, or metabolic disorders.
- Genetics: Family history of kidney stones.
- Medications: Certain diuretics or calcium supplements.
Types of Kidney Stones
- Calcium Stones: The most common, often calcium oxalate or calcium phosphate.
- Striate Stones: Associated with urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Uric Acid Stones: Often related to high-protein diets or gout.
- Cystine Stones: Rare, caused by a hereditary disorder.
Symptoms
- Severe pain in the lower back or side (renal colic).
- Haematuria (blood in urine).
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine.
Diagnosis
- Imaging: Ultrasound, CT scan, X-rays.
- Blood tests: To check calcium or uric acid levels.
- Urine tests: To detect crystal-forming substances.
Ayurvedic Perspective on Kidney Stones
Concept in Ayurveda
Kidney stones are referred to as "Mutrashmari", meaning "urinary calculi." It is considered a Krichchrasadhya (difficult-to-treat) condition caused by an imbalance in Vata, Pitta, and Kapha doshas, with Kapha and Vata often playing dominant roles.
Causes
- Excessive consumption of heavy, oily, and cold foods.
- Drinking unclean or low quantities of water.
- Suppression of natural urges (e.g., urination).
- Excessive intake of acidic, spicy, or salty foods.
Symptoms (Lakshanas)
- Pain in the lower abdomen and groin.
- Burning sensation during urination.
- Frequent urination with difficulty.
- Haematuria (Rakta Mutra).
Treatment Approach
1. Shodhana Chikitsa (Detoxification)
- Virechana (Purgation): To eliminate toxins.
- Basti (Medicated Enemas): For balancing Vata dosha.
Herbal formulations:
Varunadi Kashaya:
Dissolves stones and prevents recurrence.
Gokshura (Tribulus terrestris):
A diuretic to flush stones.
Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa):
Reduces inflammation and supports kidney health.
Shilajit:
Renal tonic with stone-dissolving properties.
Ayurvedic formulations
- Chandraprabha Vati: Relieves urinary discomfort.
- Hajrul Yahood Bhasma: Breaks down kidney stones.
Diet and Lifestyle
Recommended Foods:
- Barley water, coconut water, and sugarcane juice.
- Light and easily digestible meals.
- Fruits like pomegranate and watermelon.
Avoid:
- Salty, sour, and spicy foods.
- Excessive milk and milk products.
- Alcohol and caffeinated beverages.
Integration of Modern and Ayurvedic Approaches
- A combined approach can often provide the best outcomes:
- Use modern diagnostic tools like ultrasound for early detection.
- Opt for Ayurvedic treatments to manage symptoms, prevent recurrence, and improve kidney health naturally
- Make lifestyle and dietary changes informed by both systems.