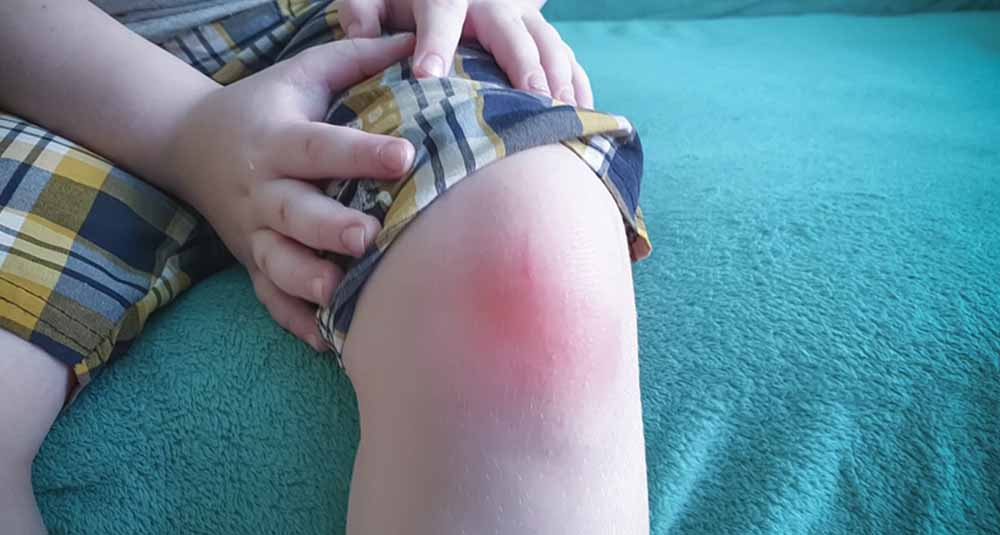
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA), now referred to as Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA), is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the joints and other tissues in children under the age of 16. It is one of the most common types of arthritis in children and can lead to long-term joint damage and disability if left untreated.
Types of JIA
JIA is classified into different subtypes based on symptoms and the number of joints affected:
1. Oligoarticular JIA
- Affects 4 or fewer joints in the first 6 months.
- Commonly affects large joints like knees or ankles.
- May cause eye inflammation (uveitis).
2. Polyarticular JIA (RF-Positive or RF-Negative)
- Affects 5 or more joints in the first 6 months.
- RF-positive resembles adult rheumatoid arthritis.
3. Systemic JIA (Still’s Disease)
- Involves fever, rash, and inflammation in multiple organs.
- May cause anaemia, enlarged lymph nodes, and hepatosplenomegaly.
4. Enthesitis-Related JIA
- Involves inflammation where tendons and ligaments attach to bones.
- Associated with back pain and sacroiliac joint involvement.
5. Psoriatic JIA
- Accompanied by psoriasis or nail changes like pitting.
6. Undifferentiated JIA
- Does not fit into any specific category.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Autoimmune Dysfunction: The immune system attacks healthy joint tissues.
- Genetic Factors: HLA genes (e.g., HLA-B27) increase susceptibility.
- Environmental Triggers: Infections or trauma may trigger onset.
- Family History: A history of autoimmune diseases increases risk.
Symptoms
- Joint pain, swelling, and stiffness (especially in the morning).
- Warmth or redness around affected joints.
- Fever and rash (in systemic JIA).
- Fatigue and reduced physical activity.
- Growth abnormalities (e.g., leg length discrepancy).
- Eye problems like uveitis or iritis.
Complications
- Joint deformities or permanent damage.
- Growth retardation due to inflammation or steroid use.
- Chronic uveitis leading to vision problems.
- Osteoporosis due to prolonged inflammation.
- Psychosocial impact (e.g., depression, anxiety).
Ayurvedic Perspective on Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
In Ayurveda, JIA can be correlated with Sahaja Aamavata or Sandhigata Vata, which occur due to an imbalance of Vata dosha combined with Ama (toxins). This imbalance disrupts the normal functioning of joints, leading to pain and inflammation.
Symptoms in Ayurveda
- Pain and stiffness in the joints (Sandhi Shoola).
- Swelling and warmth (Shotha).
- Restricted joint mobility (Sanchaya).
- Fever (Jwara), fatigue (Daurbalya), and loss of appetite (Aruchi).
Ayurvedic Treatment
Detoxification (Shodhana)
- Virechana (Purgation): To eliminate Ama and balance Pitta.
- Basti (Medicated Enema): Especially Anuvasana Basti (oil enema) and Niruha Basti (decoction enema) to pacify Vata.
Panchakarma Therapies
- Abhyanga (Oil Massage): Using medicated oils like Mahanarayan Taila or Dhanwantharam Taila.
- Swedana (Herbal Fomentation): Relieves stiffness and improves mobility.
- Janu Basti: Retaining warm medicated oil over the knee joints.
- Patra Pinda Sweda: Herbal poultice massage to reduce joint inflammation
Dietary Recommendations (Pathya)
- Easily Digestible Foods:
- Warm, light meals that improve digestion (e.g., khichdi, soups).
- Include spices like ginger, turmeric, and black pepper to boost Agni (digestive fire).
- Anti-inflammatory Foods: Use Haridra (turmeric), Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia), and Amla (Indian gooseberry).
Foods to Avoid (Apathya)
- Cold, heavy-to-digest foods like processed items, fried foods, and dairy products.
- Incompatible foods (Viruddha Ahara), such as milk with salty or sour items.
- Excessive intake of sour, cold, or raw foods that aggravate Vata and Ama.
Internal Medications (Shamana)
Herbal formulations help balance doshas, improve digestion, and reduce inflammation.
- Dashmool Kwath: An herbal decoction to alleviate inflammation and joint pain.
- Maha Yogaraj Guggulu: Addresses chronic joint issues and pacifies Vata.
- Rasna Saptaka Kwath: A specific formulation to relieve stiffness and swelling.
- Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia): Acts as an immunomodulator and anti-inflammatory.
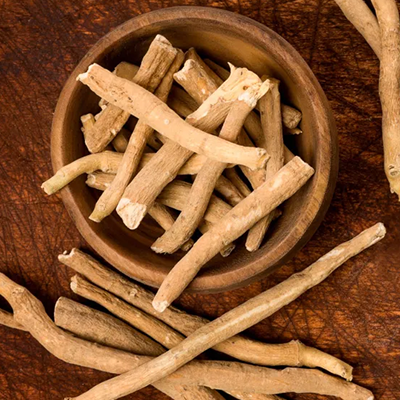
- Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera): Rejuvenates tissues and strengthens bones and joints.
- Eranda Taila (Castor Oil): Helps in purgation and reduces joint stiffness.
Rejuvenation Therapy (Rasayana)
Rasayana :
therapies focus on tissue regeneration, immunity enhancement, and long-term management.
Chyawanprash :
A herbal formulation to improve immunity and energy.
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera):
Strengthens joints and muscles.
Shatavari (Asparagus racemosus):
Supports tissue nourishment and balances Vata-Pitta.
Guggulu :
Preparations (e.g., Yogaraj Guggulu): To rebuild cartilage and improve joint mobility.
Yoga and Pranayama
Yoga and breathing techniques enhance flexibility, strengthen muscles, and improve overall wellbeing.
In Ayurveda, JRA is managed holistically by addressing both the root cause (Ama and dosha imbalance) and symptoms (joint pain and inflammation). A combination of detoxification, internal medications, lifestyle modifications, and rejuvenation therapies offers a sustainable and natural approach to managing this condition.