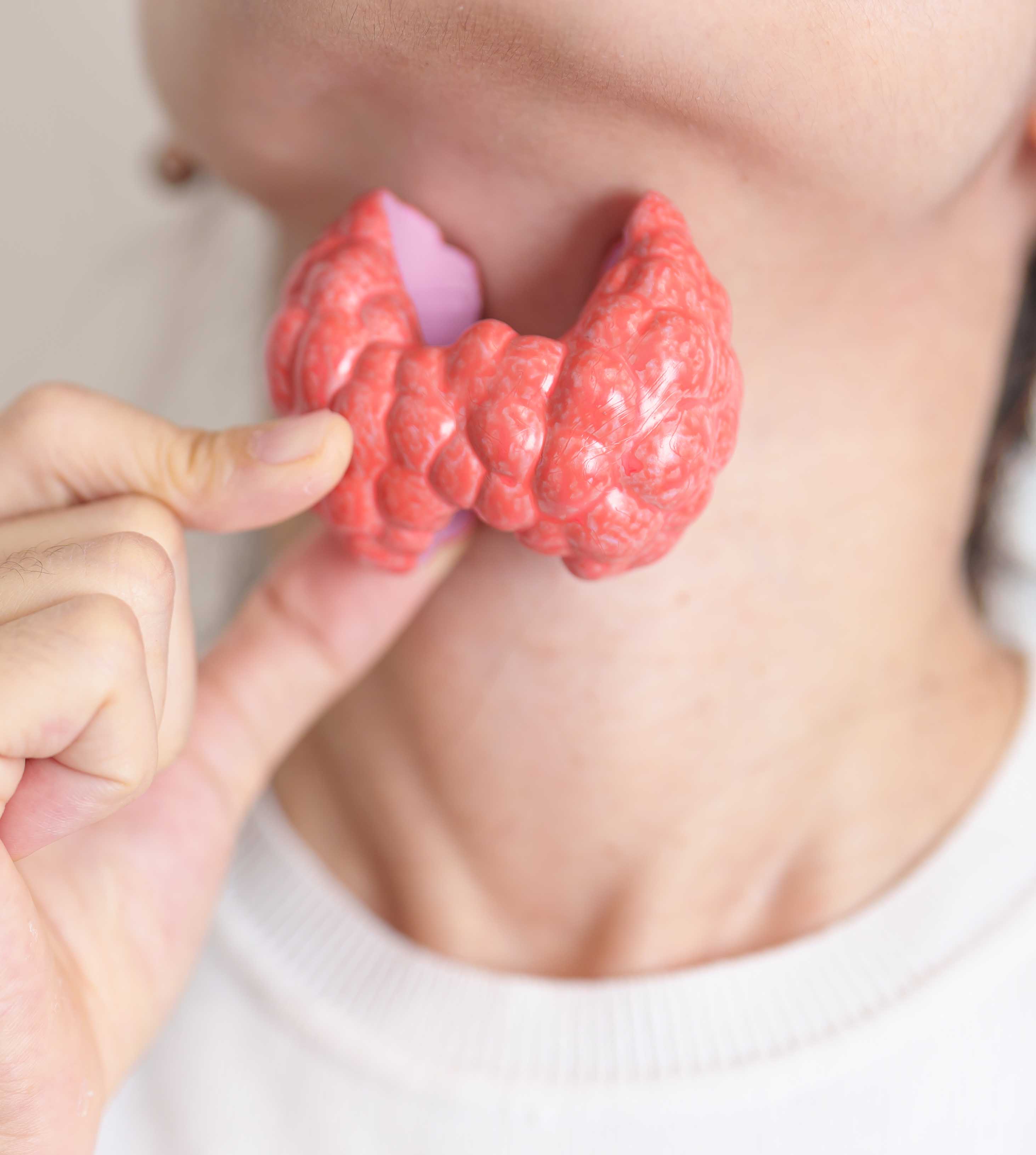
Hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland (a small, butterfly-shaped gland in the neck) does not produce enough thyroid hormones to meet the body’s needs. Thyroid hormones regulate many body processes, including metabolism, energy production, and body temperature.
When these hormones are insufficient, the body's metabolism slows down, causing a wide range of symptoms. It is more common in women, especially those over 50 years old.
How Does the Thyroid Gland Work?
The thyroid gland produces two primary hormones:
- T3 (Triiodothyronine)
- T4 (Thyroxine)
These hormones are controlled by the pituitary gland through TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone). In hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough T3 and T4, often causing TSH levels to rise as the body tries to stimulate the thyroid.
What Happens in Hypothyroidism?
1. Slow Metabolism:
Reduced thyroid hormones slow down the body’s ability to convert food into energy.
2. Impaired Organ Function:
Muscles, heart, and brain slow down due to reduced energy availability.
3. Accumulation of Fluids and Fats:
Weight gain, puffiness, and swelling (especially in the face) occur.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Weight gain despite no changes in diet.
- Dry skin and hair loss.
- Cold intolerance (always feeling cold).
- Constipation.
- Depression or low mood.
- Hoarseness of voice.
- Puffy face and swollen hands or feet.
- Slow heart rate.
- Menstrual irregularities or infertility in women.
Causes of Hypothyroidism
- Autoimmune Disorders: The most common cause is Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis, where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland.
- Iodine Deficiency: Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production, and a lack of it leads to hypothyroidism.
- Post-Thyroid Surgery or Radiation: Removing or damaging the thyroid gland can cause hormone deficiency.
- Medications: Drugs like lithium or amiodarone can interfere with thyroid function.
- Congenital Hypothyroidism: Some are born with an underactive thyroid gland.
Complications of Hypothyroidism
- Goitre: Enlargement of the thyroid gland due to overstimulation by TSH.
- Heart Problems: Elevated cholesterol levels increase the risk of heart disease.
- Infertility: Hormonal imbalances affect ovulation and fertility.
- Myxoedema: Severe hypothyroidism causing life-threatening symptoms like low body temperature and coma.
- Developmental Delays (in children): Intellectual and growth issues if untreated.
Ayurvedic Perspective on Hypothyroidism
In Ayurveda, hypothyroidism is related to an imbalance of the Kapha Dosha (which governs structure, lubrication, and stability) and Agni (digestive fire). The condition is often linked to Agnimandya (weakened digestion) and Dhatu Shaithilya (impaired tissue metabolism).
Panchakarma Therapy
- Vamana (Emesis Therapy): Cleansing Kapha from the body.
- Virechana (Purgation Therapy): Removes toxins and balances Pitta and Kapha.
- Abhyanga (Oil Massage): Improves circulation and metabolism.
Dietary Guidelines
Foods to Include:
- Warm, light, and easily digestible foods like soups, ginger tea, and seasonal fruits.
- Selenium-rich foods (nuts and seeds) and iodine sources like seaweed.
Foods to Avoid:
- Cold, heavy, or processed foods.
- Cabbage, cauliflower, and soy, which can inhibit thyroid function.
Lifestyle Recommendations
- Exercise: Moderate activity like yoga or brisk walking improves circulation and reduces Kapha.
- Yoga for Hypothyroidism: Poses like Sarvangasana (Shoulder Stand), Halasana (Plow Pose), and Matsyasana (Fish Pose) stimulate the thyroid gland.
- Pranayama: Breathing exercises like Ujjayi and Kapalabhati enhance metabolism.
- Stress Management: Meditation and mindfulness help balance Vata and reduce stress-related hormonal imbalances.
Herbal Remedies
Kanchnar Guggulu:
A classical Ayurvedic medicine to support thyroid health and reduce Kapha accumulation.
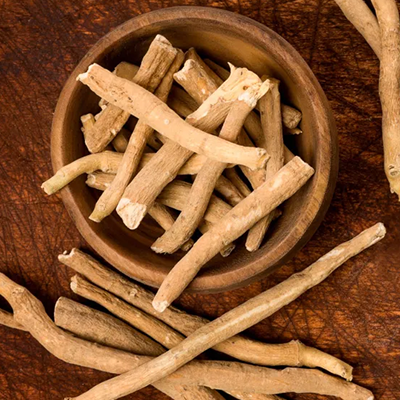
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera):
Adaptogenic herb that balances hormones and supports thyroid function.
Triphala :
Detoxifies the digestive system and improves metabolism.
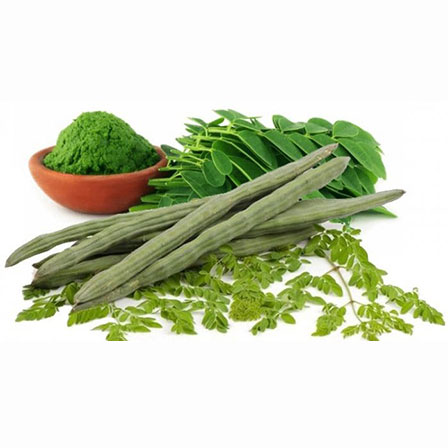
Shigru (Moringa oleifera):
Enhances metabolism and supports thyroid health.
Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa):
Diuretic and Kapha-reducing properties help manage swelling and sluggishness.
Hypothyroidism is a manageable condition with appropriate care. While modern medicine provides reliable hormone replacement therapy, Ayurveda offers a natural, holistic approach to address root causes and improve overall well-being. Combining both approaches—modern medication and Ayurvedic lifestyle changes—can optimize thyroid health and enhance quality of life.