Hypotension, or low blood pressure, occurs when the blood pressure in your arteries is lower than normal. Blood pressure is measured in two numbers:
- Systolic Pressure: The pressure when your heart beats.
- Diastolic Pressure: The pressure when your heart rests between beats.
Normal blood pressure is around 120/80 mmHg. Hypotension is generally defined as blood pressure below 90/60 mmHg. While it may not always be a cause for concern, chronic or severe hypotension can deprive the body’s organs of enough blood and oxygen, leading to serious complications.
What Happens in Hypotension?
- Reduced Blood Flow: Blood circulation to vital organs like the brain, heart, and kidneys decreases.
- Oxygen and Nutrient Deficiency: The organs may not function properly due to insufficient oxygen and nutrients.
- Symptoms of Poor Circulation: Feeling dizzy, faint, or fatigued.
Symptoms of Hypotension
- Dizziness or light headedness.
- Fainting (syncope).
- Blurred or dim vision.
- Fatigue or weakness.
- Nausea.
- Cold, clammy, or pale skin.
- Rapid or shallow breathing.
Causes of Hypotension
- Dehydration: Losing too much water from the body reduces blood volume.
- Heart Problems: Weak heart pumping (heart failure) or slow heart rate (bradycardia).
- Endocrine Disorders: Hormonal imbalances (e.g., adrenal insufficiency, diabetes).
- Blood Loss: Severe injuries or internal bleeding reduce blood pressure.
- Medications: Diuretics, blood pressure medications, or antidepressants can lower blood pressure.
- Shock or Severe Infection: In cases like septic shock, blood pressure drops dangerously low.
- Postural Changes: Sudden standing up (orthostatic hypotension) can cause dizziness
Risks and Complications of Hypotension
- Falls and Injuries: Dizziness or fainting increases the risk of falls.
- Shock: Extremely low blood pressure can lead to organ failure.
- Brain Damage: Prolonged oxygen deficiency can impair brain function.
Ayurvedic Perspective on Hypotension
In Ayurveda, hypotension is linked to an imbalance in Vata Dosha (responsible for movement and circulation) and Rakta Dhatu Kshaya (deficiency or weakness in blood tissue). Weak digestion, poor circulation, or an improper diet and lifestyle can aggravate Vata, leading to low blood pressure.
Ayurvedic Treatment for Hypotension
Ayurveda aims to balance Vata Dosha, nourish the blood (Rakta Dhatu), and strengthen the digestive fire (Agni).
Panchakarma Therapies
- Abhyanga (Oil Massage): Warm oil massages improve circulation and calm Vata.
- Shirodhara: Pouring medicated oil on the forehead relaxes the mind and balances Vata.
Dietary Guidelines
Foods to Include:
- Warm, easily digestible, and nourishing foods like soups, stews, and ghee.
- Iron-rich foods like dates, pomegranate, and leafy greens to strengthen Rakta Dhatu.
- Herbal teas with ginger or cardamom to stimulate circulation.
Foods to Avoid:
- Cold, raw, or dry foods that aggravate Vata.
- Overly light or fasting diets.
Lifestyle Recommendations
- Yoga: Gentle poses like Viparita Karani (Legs-Up-the-Wall Pose) and Balasana (Child’s Pose) improve circulation.
- Pranayama: Breathing exercises like Nadi Shodhana and Bhramari calm the mind and stabilize blood flow.
- Hydration: Drinking warm water with a pinch of salt improves blood volume.
Rasayanas (Rejuvenation Therapies)
Consuming Ayurvedic tonics like Chyawanprash or Dashmoolarishta boosts overall vitality.
Herbal Remedies
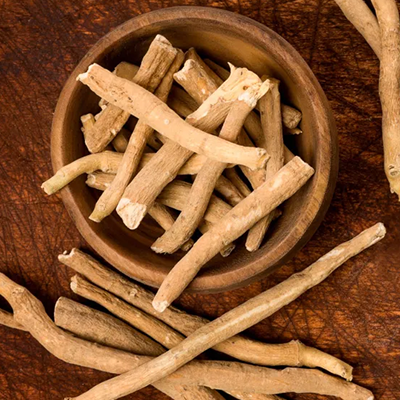
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera):
Strengthens the body and reduces fatigue.
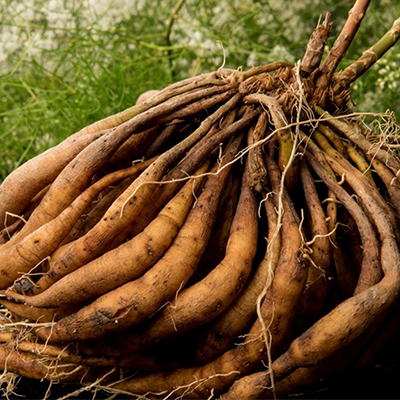
Shatavari (Asparagus racemosus):
Improves energy and balances Vata.
Arjuna (Terminalia arjuna):
Supports heart health and circulation.
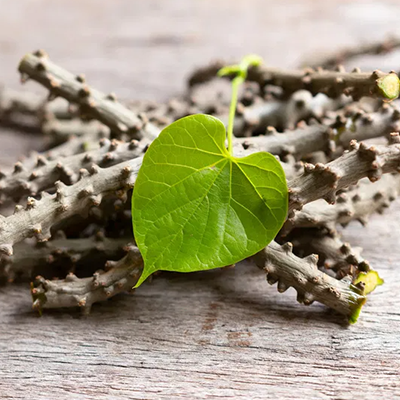
Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia):
Enhances immunity and nourishes the body.
Licorice (Yashtimadhu):
Helps stabilize blood pressure by strengthening the adrenal glands.
Hypotension, though not always dangerous, can cause significant discomfort and lead to complications if untreated. Modern medicine addresses the symptoms and underlying causes effectively, while Ayurveda provides a natural and holistic approach to restoring balance in the body. A combination of dietary changes, herbal remedies, and lifestyle adjustments can help manage low blood