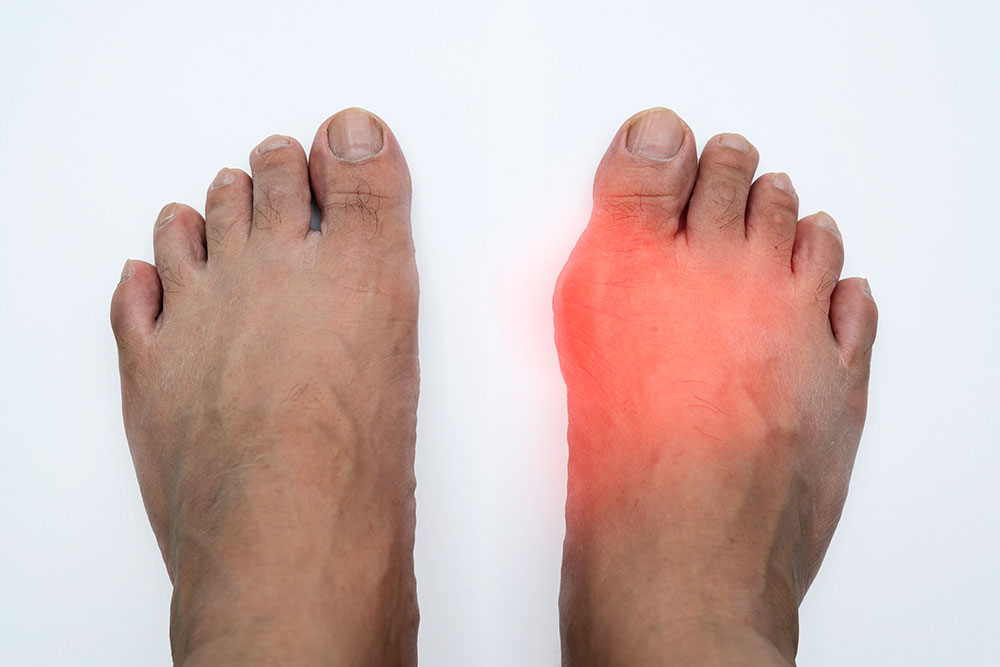
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to sudden, severe pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness. Uric acid is a by-product of purine metabolism, and when its levels exceed the body’s capacity to excrete it, it crystallizes in the joints and surrounding tissues.
Who Does Gout Affect the Most?
Gout typically affects:
- Middle-aged and older adults: More common in men (30-50 years), but women become more susceptible after menopause.
- Individuals with a family history: A genetic predisposition increases the risk.
- More common in people who have a sedentary lifestyle
Causes of Gout:
Dietary Habits:
- High consumption of purine-rich foods (red meat, organ meats, shellfish).
- Excessive alcohol intake, especially beer.
- Sugary beverages and fructose-rich foods.
Lifestyle Factors:
- Sedentary lifestyle and obesity.
- Dehydration or low water intake.
Medical Conditions:
- Kidney dysfunction (reduced uric acid excretion).
- Hypertension and cardiovascular diseases.
- Diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
Signs and Symptoms of Gout
Gout symptoms often appear suddenly, frequently at night, and may affect a single joint initially.
Acute Gout Attack Symptoms:
- Intense joint pain (commonly in the big toe, but can affect ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers).
- Swelling and tenderness in the affected joint.
- Redness and warmth over the joint.
- Limited range of motion.
Chronic Symptoms (if untreated):
- Formation of tophi (hard uric acid deposits under the skin).
- Persistent joint discomfort.
- Joint deformities or damage.
Complications of Gout
1. Tophaceous Gout:
- Development of tophi, which can cause disfigurement and pain.
2. Chronic Arthritis:
- Long-term inflammation and joint damage.
3. Kidney Stones:
- Uric acid crystallization in the kidneys.
4. Cardiovascular Risks:
- Increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
5. Joint Damage:
- Advanced cases may cause permanent disability.
Diagnosis of Gout:
1. Clinical Examination:
Assessment of symptoms and affected joints.
2. Laboratory Tests:
- Serum Uric Acid Levels: Elevated uric acid (>6.8 mg/dL).
- Synovial Fluid Analysis: Presence of urate crystals under a microscope.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): To check for signs of infection or inflammation.
3. Imaging Studies:
- X-ray: To assess joint damage in chronic cases.
- Ultrasound: Detects urate crystals in joints and soft tissues.
- Dual-Energy CT (DECT): For advanced crystal detection.
Ayurvedic Perspective on Gout
In Ayurveda, gout is correlated with Vatarakta, a condition caused by the vitiation of Vata dosha and accumulation of toxins (Ama) in the blood (Rakta dhatu). It affects the joints and blood circulation, leading to inflammation and pain.
Ayurvedic Treatment for Gout
The Ayurvedic approach involves detoxification, dosha balancing, improving digestion, and reducing inflammation.
Shodhana (Detoxification):
- Virechana (Purgation): Removes toxins and balances Pitta.
- Raktamokshana (Bloodletting): Effective for severe inflammation.
Dietary Guidelines:
- Avoid purine-rich foods, red meat, alcohol, and processed foods.
- Include cooling foods like barley, cucumber, and coconut water.
- Consume digestive spices like cumin, coriander, and fennel.
Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Regular physical activity to improve metabolism.
- Stress management through yoga and pranayama.
- Maintain hydration to flush out uric acid.
External Therapies:
- Lepa (Herbal Paste): Apply paste made of turmeric and sandalwood to reduce joint swelling.
- Abhyanga (Oil Massage): Use medicated oils like Dashamoola Taila or Mahanarayan Taila.
- Basti (Enema): Medicated enema to balance Vata and improve digestion.
Ayurvedic Formulations:
- Kaishore Guggulu: Treats inflammation and purifies blood.
- Triphala: Improves digestion and prevents Ama formation.
- Chandraprabha Vati: Enhances kidney function and uric acid excretion.
- Punarnavadi Kashaya: Reduces swelling and supports detoxification.
Herbal Remedies:
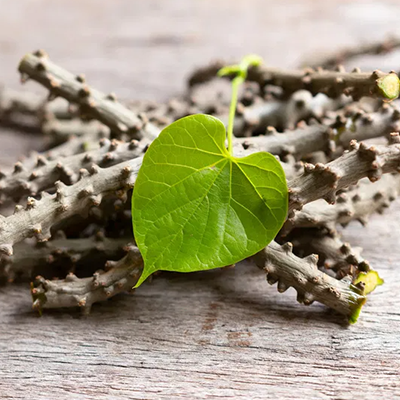
Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia):
Anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating.
Guggulu (Commiphora mukul):
Reduces swelling and joint pain.
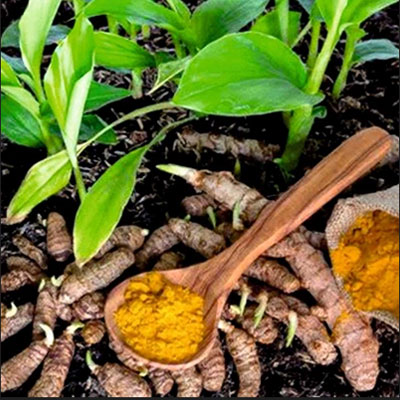
Haridra (Turmeric):
Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant.
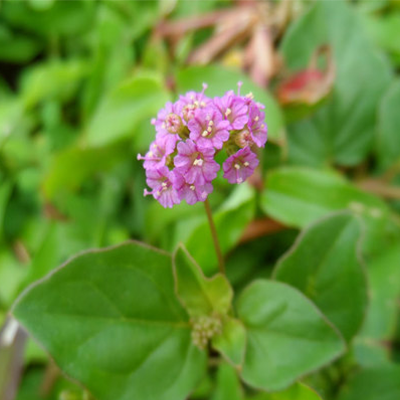
Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa):
Diuretic and detoxifying.
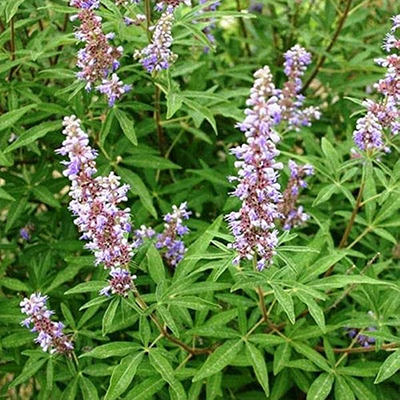
Nirgundi (Vitex negundo):
Relieves pain and inflammation.