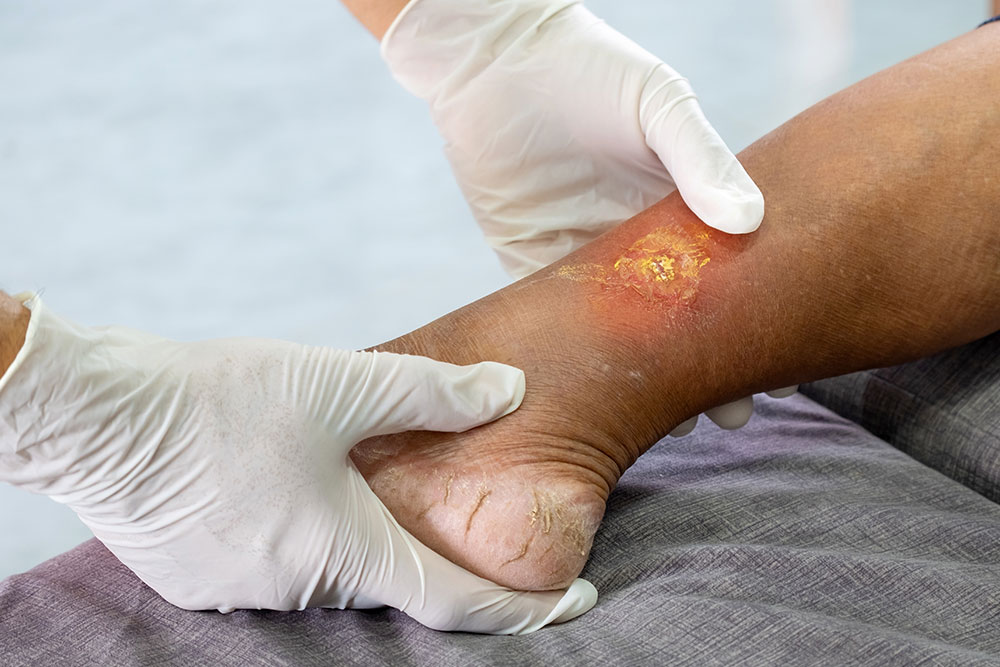
Gangrene is the death of body tissue due to a lack of blood supply or severe bacterial infection. It is a medical emergency requiring immediate attention to prevent the spread of dead tissue and infection to other parts of the body.
Causes of Gangrene
Gangrene develops when the blood supply to a specific area is disrupted, leading to tissue death. Common causes include:
1. Reduced Blood Flow:
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
- Atherosclerosis (narrowing of arteries)
- Blood clots
2. Infections:
- Severe bacterial infections, especially from wounds or injuries.
- Diabetic ulcers that become infected.
3. Trauma or Injury:
- Burns, frostbite, or crush injuries that damage blood vessels.
4. Chronic Conditions:
- Diabetes, which causes poor circulation and nerve damage.
- Immune system disorders or cancer treatments.
Types of Gangrene
1. Dry Gangrene:
- Caused by reduced blood flow to the area.
- Tissue becomes dry, shrivelled, and black.
- Commonly affects extremities like fingers, toes, and limbs.
2. Wet Gangrene:
- Occurs with bacterial infection.
- Tissue appears swollen, moist, and emits a foul smell.
- Often seen in diabetic ulcers or infected wounds.
3. Gas Gangrene:
- Caused by Clostridium bacteria that produce gas within the tissue.
- Tissue becomes pale, swollen, and produces gas bubbles.
- Life-threatening and requires immediate treatment.
4. Internal Gangrene:
- Affects internal organs like the intestines or gallbladder.
- Associated with severe pain and systemic symptoms like fever.
5. Fournier's Gangrene:
- Affects the genital area, often caused by bacterial infections.
Signs and Symptoms of Gangrene
Local Symptoms:
- Pain followed by numbness.
- Skin discoloration (red, purple, black, or green)
- Swelling or blisters.
- Foul-smelling discharge (in wet gangrene).
Systemic Symptoms:
- Fever, chills, or sweating.
- Rapid heartbeat.
- Shock in advanced stages.
Complications Associated with Gangrene
1. Septicemia (Blood Infection):
Infection spreads into the bloodstream, causing systemic inflammation and organ failure.
2. Amputation:
Removal of the affected limb to prevent the spread of gangrene.
3. Organ Failure:
In cases of internal gangrene, vital organs may fail.
4. Life-threatening Infections:
Gas gangrene can cause rapid tissue destruction and death if untreated.
Ayurveda identifies it as a condition of Srotorodha (blockage of channels), leading to reduced blood supply, accumulation of toxins (ama), and tissue death.
Ayurvedic Treatment for Gangrene
Ayurvedic treatment focuses on improving circulation, detoxification, and wound healing while preventing further tissue damage and infection.
Detoxification (Shodhana):
- Raktamokshana (Bloodletting): To remove stagnated blood and toxins.
- Virechana (Purgation): Balances Pitta and detoxifies the system.
- Leeches (Jalaukavacharana): Used to improve blood flow to the affected area.
Wound Management (Vrana Chikitsa):
Topical Applications:
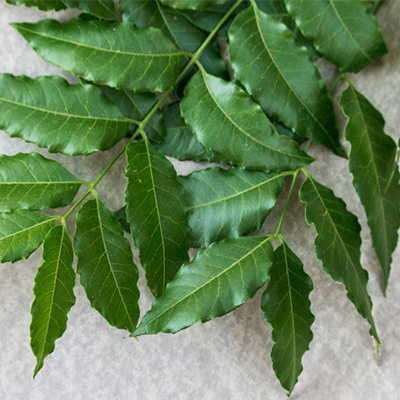
Neem (Azadirachta indica):
Antibacterial and antiseptic.
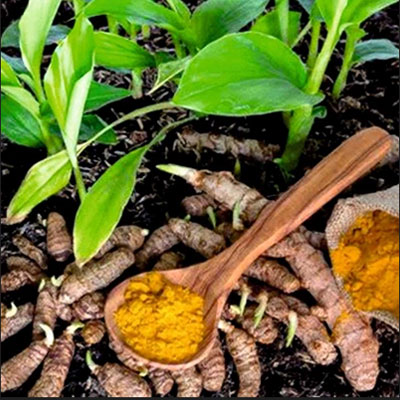
Haridra (Turmeric):
Anti-inflammatory and wound-healing properties.
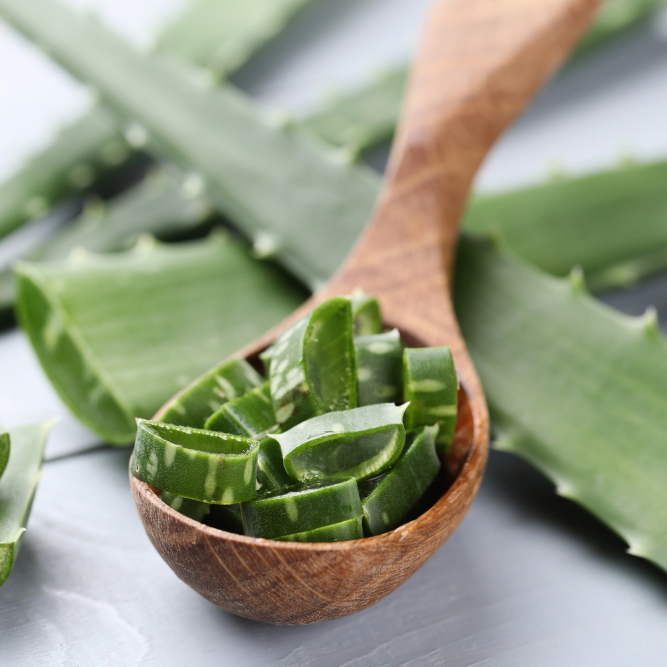
Aloe Vera (Kumari):
Promotes tissue repair.
Manjistha (Rubia cordifolia):
Cleanses blood and accelerates healing.
Medicated Oils and Pastes:
- Jatyadi Taila: Effective for cleaning and healing wounds.
- Panchavalkala Kwatha: Used as a wound wash.
Internal Medications:
- Triphala Guggulu: Reduces inflammation and promotes wound healing.
- Khadirarishta: Purifies blood and combats infections.
- Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera): Improves tissue regeneration.
Herbs to Improve Circulation and Immunity:
- Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia): Detoxifies and boosts immunity.
- Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri): Improves microcirculation.
- Ashoka (Saraca asoca): Supports vascular health.
Diet and Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Avoid cold, oily, and heavy foods.
- Include bitter and astringent foods (e.g., neem, karela).
- Eat easily digestible, freshly cooked meals.
- Maintain hygiene of the affected area.
- Engage in light physical activity to improve blood flow.
Preventive Measures in Ayurveda
1. Maintain Healthy Circulation:
Regular massage with medicated oils (e.g., sesame oil) to promote blood flow.
2. Boost Immunity:
Use Rasayana herbs like Amalaki, Haritaki, and Ashwagandha.
3. Manage Chronic Conditions:
Control diabetes and other underlying disorders.
4. Avoid Injury:
Prevent wounds in high-risk individuals (e.g., diabetics).