- +033 2572 7171
- info@dhanvantary.com

4.5 Rating | 4500 Review

4.5 Rating | 4500 Review
Blood clotting is the body’s natural way to stop bleeding after an injury. When a blood vessel gets damaged, the blood changes from a liquid to a gel-like state to form a "clot," sealing the break. This process involves small cells called platelets and various proteins that work together to control bleeding.
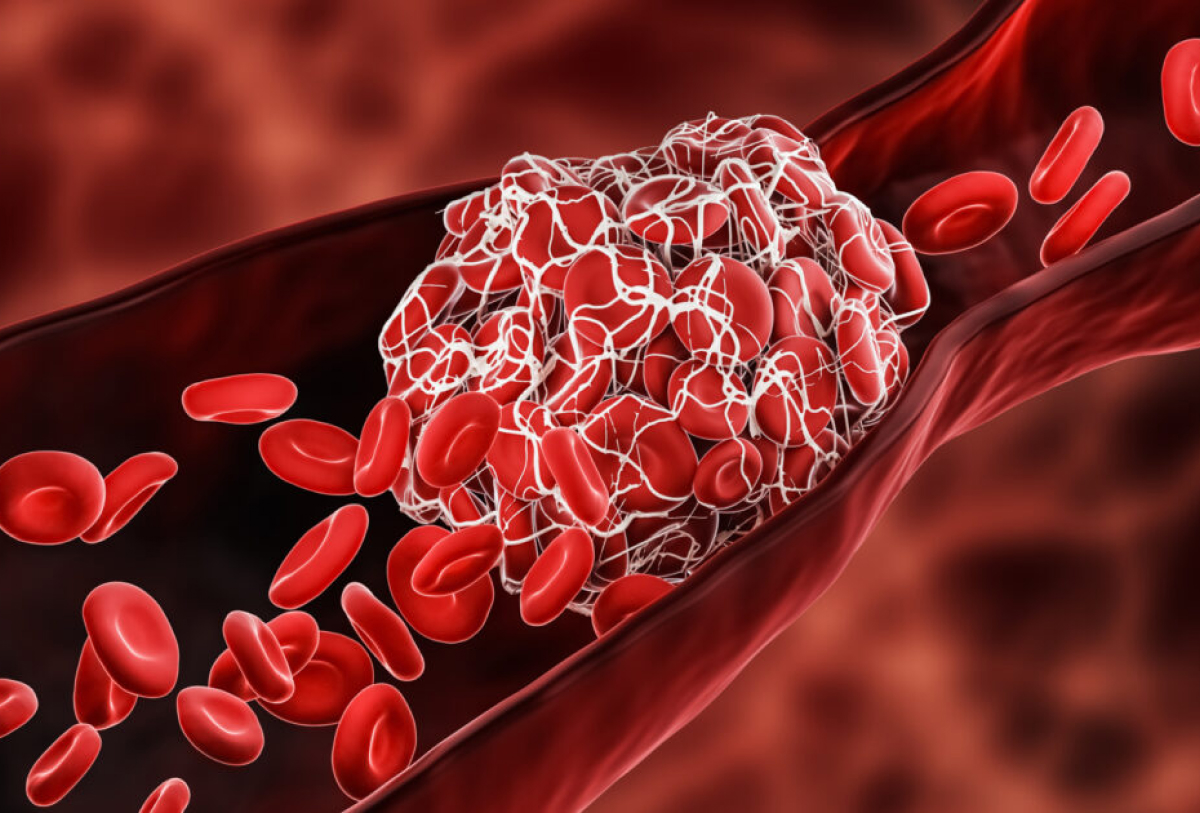
Blood clots usually form when the blood vessels are damaged, causing platelets to stick together at the injury site. This is followed by a series of reactions that help stabilize the clot. However, clots can form inappropriately, leading to serious issues if they block blood flow in major blood vessels.
A clot that forms in a deep vein, usually in the leg.
When a clot travels to the lungs, causing a blockage.
Clots that form in arteries, which can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
Clots in veins, especially in the legs or pelvis.
Sitting or lying down for long periods (like during travel or after surgery) slows blood flow and can lead to clots.
Damage to blood vessels can trigger clotting as the body tries to heal.
Certain illnesses like cancer, heart disease, or obesity make clots more likely.
Smoking, birth control pills, and obesity can increase clotting risk.
Swelling, pain, warmth, or redness in the affected area, often in the leg.
Sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, fast heartbeat, and sometimes coughing up blood.
Sharp pain, numbness, or loss of function, especially if the clot affects the heart or brain.
Clots that reach the lungs can stop oxygen from entering the blood properly, which is very dangerous.
Arterial clots in the heart or brain can stop blood flow, causing severe damage.
Pain, swelling, and skin changes that occur after having a DVT, which can be long-lasting.
Ultrasound (for DVT), and CT scan (for PE) are common tools.
A D-dimer test can show signs of clot fragments in the blood.
In some cases, doctors use other scans or genetic tests to identify clotting risks.
In Ayurveda, blood clotting or "rakta stambhana" is seen as a disruption in the natural flow of blood, often due to imbalances in the doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha), as well as improper digestion (Agni) and accumulation of toxins (Ama). This view aligns with a holistic perspective, focusing on the underlying lifestyle, dietary, and emotional factors that contribute to the condition.
Panchakarma detox therapies, such as Virechana (therapeutic purgation) and Basti (medicated enema), are often recommended to remove toxins, cleanse the blood, and balance doshas, especially in those prone to clotting.
Eat light, warm, and easily digestible foods to enhance Agni and reduce Ama build-up. Avoid heavy, oily, and processed foods.
Incorporate dosha-specific foods: For Kapha, reduce dairy and fried foods; for Pitta, avoid overly spicy foods; for Vata, favour grounding and warm foods.
Drink warm water with lemon or ginger throughout the day to keep circulation active.
Gentle yoga and breathing exercises like Anulom Vilom (alternate nostril breathing) and Bhramari Pranayama help improve circulation, reduce stress, and balance Vata and Pitta, supporting healthy blood flow.
Practice meditation and mindfulness to keep Vata in balance and reduce stress-related inflammation, which can contribute to clotting risks.
Engaging in daily, moderate exercise helps reduce Ama and promotes good blood circulation, essential for preventing blood clots.
Drinking adequate water supports blood flow and prevents blood from thickening.
Regular movement is key, especially during long periods of sitting, such as during travel or office work.
Ayurveda encourages balancing rest with activity to support healthy blood flow.
By integrating these Ayurvedic herbs, dietary changes, and lifestyle practices, one can support healthy blood circulation, minimize the risk of blood clots, and promote overall vascular health. However, these treatments should be used under the guidance of a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner, especially when blood clotting issues are already present.
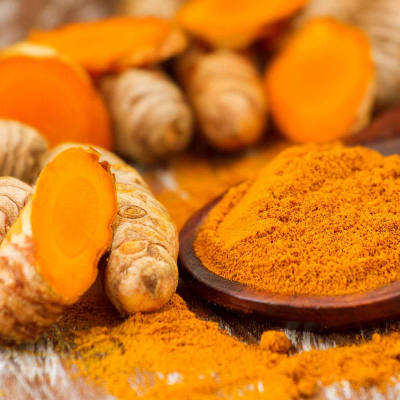

Known for its anti-inflammatory and blood-thinning properties, turmeric is high in curcumin, which supports circulation, reduces inflammation, and prevents clot formation. It can be consumed in food, teas, or as a supplement.

Arjuna is an Ayurvedic herb specifically beneficial for heart health. It helps strengthen blood vessels, improves circulation, and has mild blood-thinning properties. It can be taken as a powder or in capsules.
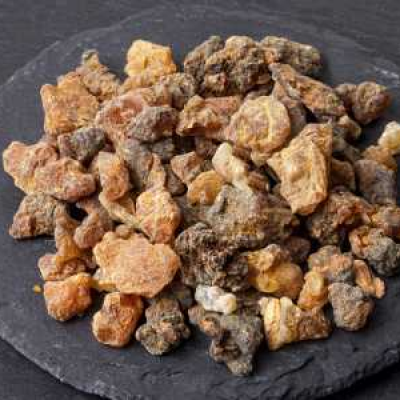

Guggul supports metabolism, reduces cholesterol, and helps dissolve clots by breaking down Ama (toxins). Its anti-inflammatory properties also reduce plaque build-up in the arteries, promoting smoother blood flow.
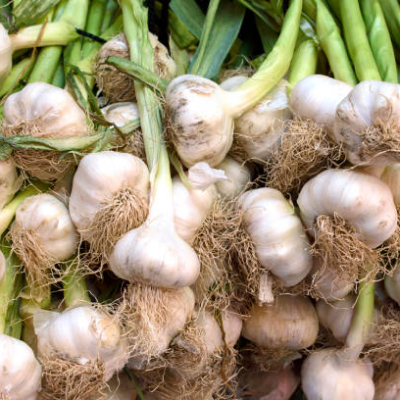

Garlic is a well-known anticoagulant that helps reduce blood viscosity, improve circulation, and lower cholesterol. It can be eaten raw or taken as a supplement.
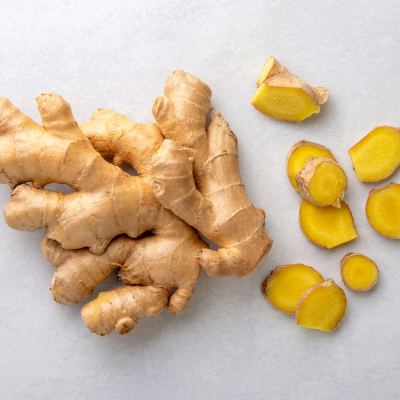

Ginger has blood-thinning properties that improve circulation. It also reduces inflammation and clears toxins from the body. Ginger tea or fresh ginger can be included in the diet.
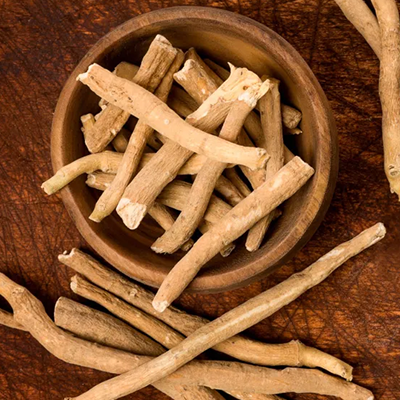

Known to reduce stress, ashwagandha helps balance Vata and reduces inflammation in the blood vessels, which can aid in preventing clot formation.
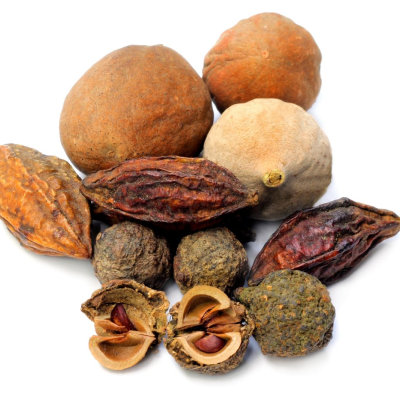

Triphala, a combination of three fruits (Haritaki, Amalaki, and Bibhitaki), is a gentle detoxifying formula that helps cleanse the body and improve digestion, preventing the accumulation of Ama, which can contribute to clot formation.
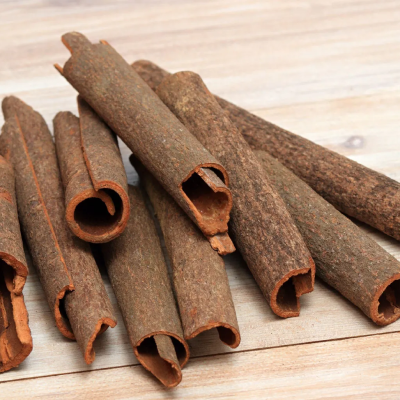

Cinnamon has blood-thinning effects and improves circulation. It is also an anti-inflammatory and helps regulate blood sugar levels, which is beneficial for overall vascular health.
