- +033 2572 7171
- info@dhanvantary.com

4.5 Rating | 4500 Review

4.5 Rating | 4500 Review
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), often referred to as an enlarged prostate, is a common condition in men as they age. It’s called “benign” because it’s not cancerous. The prostate is a small gland located below the bladder and around the urethra (the tube that carries urine out of the body). When the prostate enlarges, it can press on the urethra, making it harder for urine to pass.
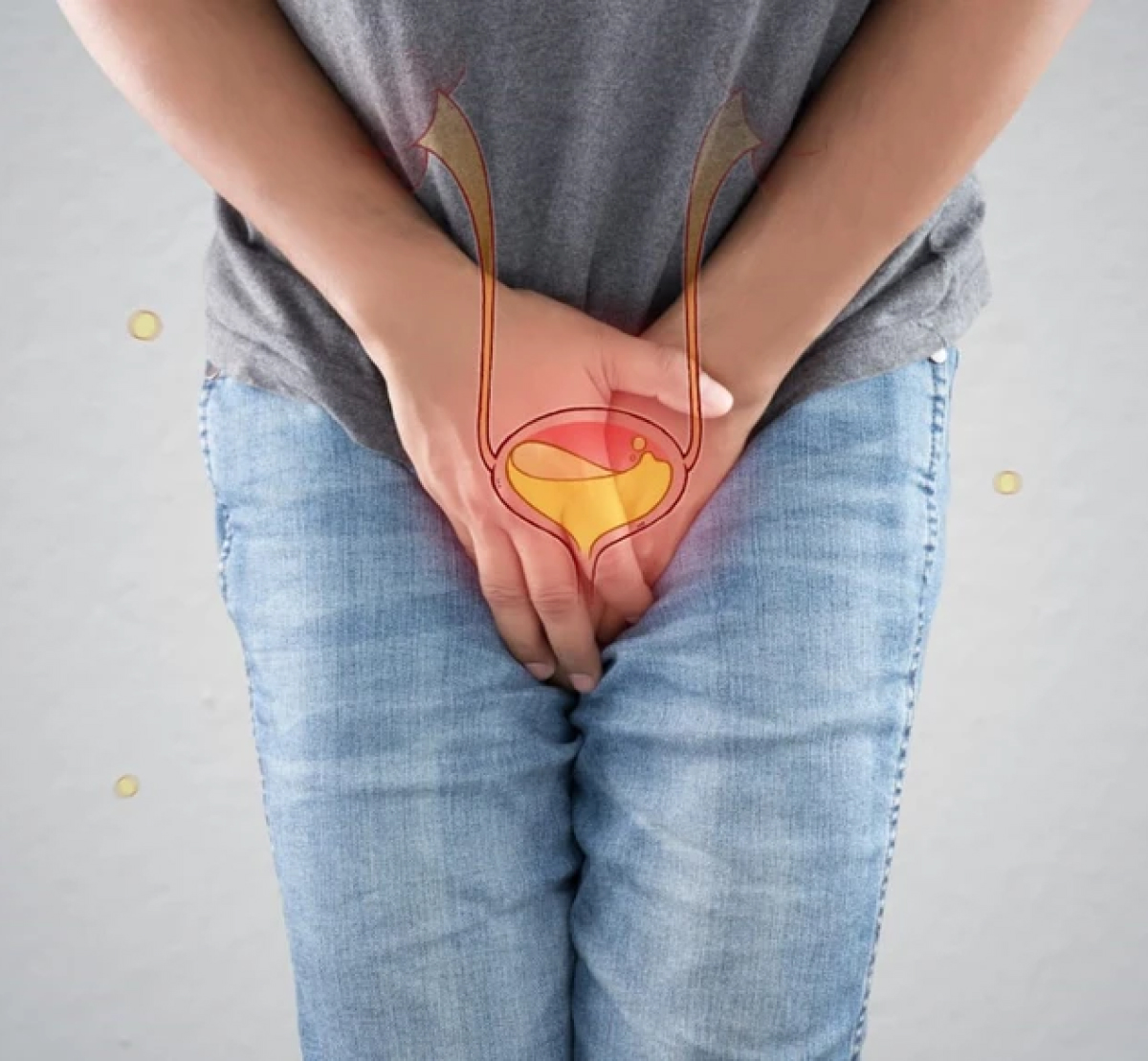
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is most commonly seen in men over the age of 50.
BPH is primarily age-related, with hormonal changes playing a significant role in prostate enlargement as men get older.
Bell's palsy occurs when there is inflammation or compression of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII), which controls the muscles of the face. This inflammation disrupts the signals from the brain to the facial muscles, leading to weakness or paralysis on one side.
The exact cause of BPH isn’t fully understood, but it’s likely related to hormonal changes as men get older. As men age, their levels of testosterone and estrogen change, which can lead to prostate growth.
Aging : BPH is most common in men over 50.
Family history : If a close relative had BPH, there’s a higher chance of developing it.
Lifestyle factors : Obesity, lack of exercise, and certain diets may increase the risk.
Infection from these viruses can cause swelling of the facial nerve, leading to the symptoms of Bell's palsy.
BPH affects urination because the enlarged prostate squeezes the urethra.
Common symptoms include:
Especially at night (nocturia), which can disrupt sleep.
Feeling a strong urge to go but difficulty in starting.
Slow or weak flow of urine, often starting and stopping.
Feeling like the bladder hasn’t fully emptied.
Leaking a bit of urine after finishing.
If left untreated, BPH can lead to complications such as :
Complete inability to urinate, requiring immediate medical help.
Bacteria can grow if urine remains in the bladder.
Pressure from retained urine can weaken the bladder walls.
Long-term urinary retention can put stress on the kidneys.
According to Ayurveda, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is understood through an imbalance in the Vata and Pitta doshas, particularly affecting the urinary system and reproductive organs. This condition is often referred to as Mutraghata or Mutrakrichra, which relate to urinary retention and difficulty in urination. Ayurveda treats BPH by addressing dosha imbalances, aiming to reduce inflammation, strengthen the urinary system, and promote easy flow of urine.
Include fruits like watermelon and cucumber, which have high water content, helping flush the urinary tract.
Favor easy-to-digest foods like soups, stews, and cooked vegetables. Avoid heavy, cold, and processed foods.
Spicy foods can irritate the bladder and exacerbate Pitta imbalance.
Ghee is excellent for reducing Vata, and a small amount daily can help keep the digestive system and urinary system healthy.
Both can increase the body’s water retention and worsen urinary issues.
Gentle yoga or walking can improve circulation and reduce Vata. Avoid heavy lifting, which can put pressure on the pelvic region.
Meditation and deep breathing exercises can help balance Vata and reduce stress, which is beneficial for urinary health.
Drink plenty of water, but try to limit intake in the evening to reduce night-time urination.
Frequent and complete emptying of the bladder helps avoid urinary retention.
Maintain a regular sleep schedule, as this supports all bodily systems and aids in balancing Vata.
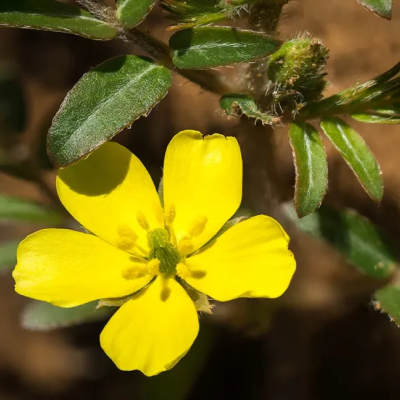

Known for its diuretic properties, Gokshura helps in reducing urinary retention and improving urine flow.
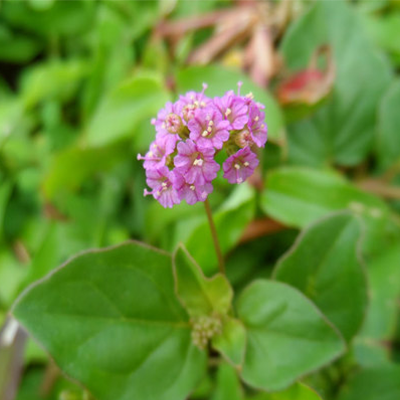

A natural diuretic, it reduces swelling and inflammation in the prostate and helps balance fluids in the body
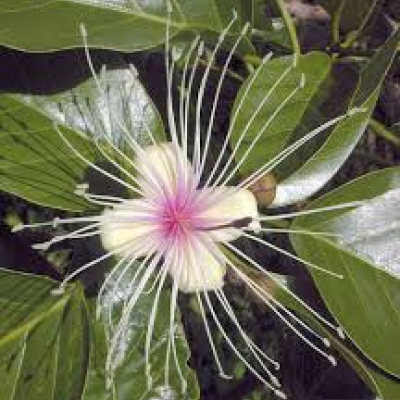

Known to improve urinary flow and reduce the size of an enlarged prostate.

A mineral-rich Ayurvedic remedy that supports the urinary system, balances Vata, and improves overall strength.

An herbal formulation that helps reduce glandular swelling and detoxifies the body.
