- +033 2572 7171
- info@dhanvantary.com

4.5 Rating | 4500 Review

4.5 Rating | 4500 Review
Atherosclerosis is a condition where the arteries (the blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood throughout the body) become thick and narrow due to a build-up of fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances. This build-up is called plaque, and it can restrict or block blood flow, leading to serious health issues.
In early stages, atherosclerosis often doesn’t show symptoms. As it worsens, symptoms can develop depending on the arteries affected:
If left untreated, atherosclerosis can lead to severe complications, including:
As per the fundamentals of Ayurveda, atherosclerosis can be interpreted as a result of an imbalance in the body’s natural energies, or doshas—Vata, Pitta, and Kapha. It’s connected to an excess of "Ama," which means toxins or impurities. These toxins are believed to build up in the body because of poor digestion, unhealthy eating habits, lack of physical activity, and stress.
When Ama accumulates, it mixes with the Kapha dosha, which can lead to blockages in the blood vessels, much like how plaque builds up in arteries in modern medicine. This restricts blood flow and affects the heart and other organs.
Detoxification (Panchakarma)
Panchakarma therapies like Virechana (therapeutic purgation) and Basti (medicated enema) are used to cleanse the body of toxins.
Svedana (herbal steam therapy): Helps open the channels and promotes circulation.
Raktamokshana (bloodletting therapy): Sometimes used to remove toxins from the blood, though it should only be done by an Ayurvedic practitioner.
Avoid Ama-producing foods: Heavy, greasy, and processed foods, as well as cold and fried foods, should be minimized, as they contribute to toxins and poor digestion.
Increase fibre intake: Eating fruits, vegetables, and whole grains helps improve digestion and eliminate toxins.
V Use heart-healthy oils like sesame or olive oil in moderation.
Include spices: Spices like turmeric, ginger, and black pepper aid in digestion and circulation.
Drink warm water: Helps in digestion and the breakdown of Ama.
Daily physical activity: Moderate exercise, like walking or yoga, improves blood flow and reduces stress.
Yoga and Pranayama: Practices like Anulom Vilom (alternate nostril breathing) and Bhujangasana (cobra pose) support heart health.
Stress management: Meditation and mindfulness practices are recommended to lower stress, which can reduce blood pressure and support heart health.

Form: Fresh fruit, powder, or juice.
Use: Amla powder can be mixed with water or taken as juice. It is rich in antioxidants and supports healthy cholesterol levels and arterial health.

Form: Powder, capsule, or in liquid extract form.
Use: Brahmi helps reduce stress and supports circulation. It can be taken as a tea, capsule, or powdered form mixed with warm water.

Form: Powder (churna), capsules, or decoction (tea).
Use: Arjuna bark powder can be mixed with warm water or milk and consumed daily. It helps in strengthening the heart, improving circulation, and reducing cholesterol.
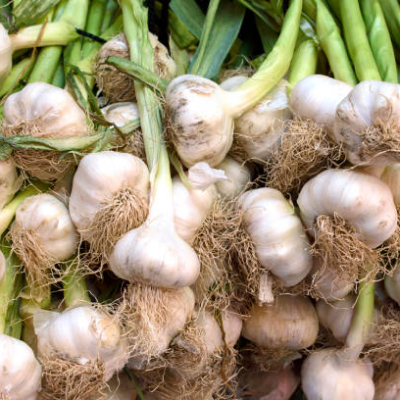

Form: Raw, powder, or capsule.
Use: Garlic is most effective when consumed raw (1-2 cloves on an empty stomach) as it helps reduce cholesterol and blood pressure. Capsules or powdered forms are also used if raw garlic is not tolerated.

Form: Powder or tablet.
Use: Taken before bed with warm water, Triphala aids in digestion and detoxification, which can help reduce toxins that may contribute to artery blockages.
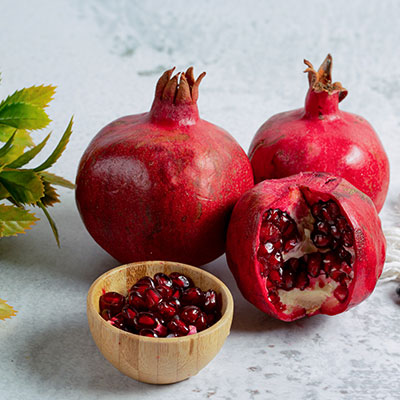

Pomegranate is loaded with antioxidants like polyphenols, tannins, and anthocyanin. These help prevent oxidative damage to the arteries, which can contribute to plaque build-up.
Some studies have suggested that pomegranate may not only prevent plaque buildup but also help reduce existing plaque in the arteries, making it unique among natural remedies.
