- +033 2572 7171
- info@dhanvantary.com

4.5 Rating | 4500 Review

4.5 Rating | 4500 Review
Asherman Syndrome is a condition where scar tissue (adhesions) forms inside the uterus. This tissue build-up can cause parts of the uterine walls to stick together, reducing or even blocking the space in the uterus. This condition can lead to menstrual problems, pain, and infertility, as the adhesions interfere with the uterine lining’s ability to function normally.
In Asherman's Syndrome, scar tissue forms within the uterus, often as a result of trauma. When this happens, the walls of the uterus may stick together in places where there is scar tissue. This can block menstrual blood flow or prevent the embryo from implanting, leading to infertility or recurrent miscarriages.
Asherman’s Syndrome is often linked to women who have undergone uterine surgery, especially a procedure called dilation and curettage (D&C). This procedure is sometimes done after a miscarriage, delivery, or abortion to clear the uterus. Other risk factors include:
The main cause is trauma to the uterus, especially following a D&C. The trauma can trigger an abnormal healing response, leading to scar tissue. Other causes include:
In Ayurveda, Asherman's syndrome may not be specifically named, but it can be interpreted based on Ayurvedic principles of reproductive health. According to Ayurveda, any reproductive issue involves an imbalance in the body’s doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha) and dhatus (tissues), particularly Artava dhatu (reproductive tissue). Asherman's syndrome could be viewed as a disturbance in the Artava vaha srotas (channels carrying reproductive tissue) due to scar formation, which disrupts the normal flow of menstruation and fertility.
Treatment generally involves surgery to remove the scar tissue and restore the uterine cavity. This can be done through a procedure called hysteroscopy, where a thin, flexible tube with a camera is used to locate and remove adhesions inside the uterus.
After treatment, women may need to be monitored to ensure the uterus heals properly, and sometimes additional therapy is recommended to improve fertility outcomes.
Panchakarma Therapy:
Procedures like Basti (medicated enema) help regulate Vata and improve reproductive organ health.
Virechana (therapeutic purgation) may help in detoxifying and balancing Pitta to reduce inflammation.
Uttarbasti: Is a specialised treatment in which herbal medicinal oils or ghritham can be administered inside the uterine cavity under strict aseptic precautions.
A Vata-Pitta balancing diet, with warm, nourishing, easily digestible foods, is recommended.
Practices like yoga, meditation, and avoiding excessive physical and mental stress are also helpful.
It’s A pinch of turmeric powder mixed with warm milk or water can be taken daily to approach Ayurveda under the supervision of a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner who can tailor treatments based on individual dosha constitution and symptoms, especially when dealing with a complex condition like Asherman’s syndrome.
In Ayurveda, certain herbs are considered beneficial for improving uterine health, reducing scar tissue, and balancing the doshas that may be involved in Asherman's syndrome. These herbs, used in various forms, can support tissue regeneration, reduce inflammation, and improve blood flow to the uterus.
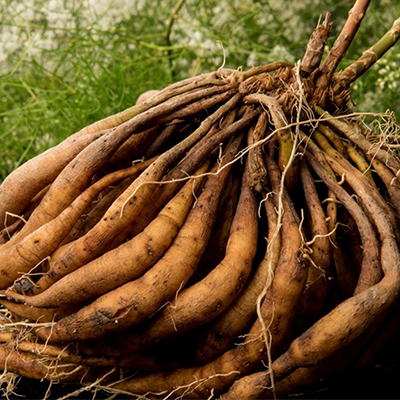

Shatavari is a nourishing and rejuvenating herb useful to support tissue growth (especially the damaged uterine lining. Shatavari powder or capsules can be taken daily, often with warm milk, which enhances its nourishing effect. A typical dose may be 1–2 teaspoons daily, but it’s best to consult an Ayurvedic practitioner for personalized dosage.
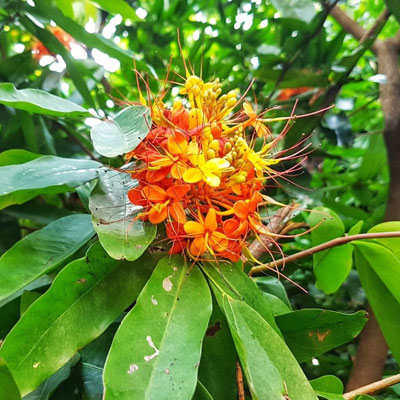

Ashoka has anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties. It is traditionally used to treat menstrual disorders and improve uterine health.
Ashoka can be consumed as a powder or decoction. Typically, 1–2 teaspoons of Ashoka powder or an Ayurvedic-formulated Ashoka syrup can be taken under guidance.
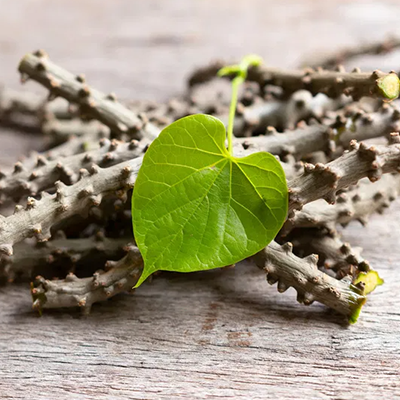

Guduchi is considered a powerful anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting herb. It supports tissue repair. It promotes cellular regeneration and helps reduce scar tissue. Its immune-supportive properties also reduce the risk of recurrent infections that might worsen adhesions.
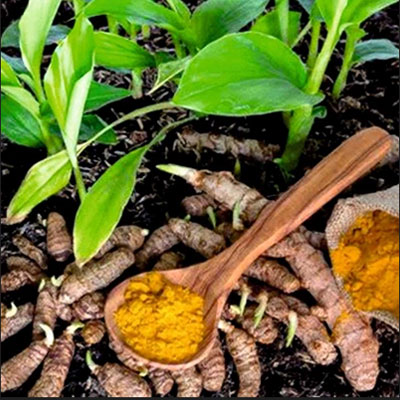

Turmeric is anti-inflammatory and aids in reducing scar tissue formation. It also supports circulation and has antimicrobial properties. A pinch of turmeric powder mixed with warm milk or water can be taken daily.
