Joint pain, medically known as arthralgia, is a common complaint that can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain. It may involve one or multiple joints and can arise from various underlying conditions.
Probable Causes of Joint Pain
Joint pain can result from multiple factors, broadly classified into inflammatory, mechanical, infectious, or systemic causes.
1. Inflammatory Causes
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune disease causing inflammation in the synovial membrane.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: Associated with psoriasis, leading to joint inflammation.
- Gout: Caused by the deposition o66gg Yhh hu 6hf uric acid crystals in joints.
- Reactive Arthritis: Triggered by infections, often of the gastrointestinal or genitourinary system.
- Lupus (SLE): An autoimmune condition affecting multiple systems, including joints.
2. Degenerative Causes
- Osteoarthritis (OA): Degeneration of cartilage due to aging or repetitive use.
- Cervical or Lumbar Spondylosis: Age-related wear of the spine causing referred joint pain.
3. Infectious Causes
- Septic Arthritis: Bacterial infection of a joint.
- Lyme disease: Joint pain caused by a tick-borne bacterial infection.
- Tubercular Arthritis: Joint infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
4. Mechanical or Traumatic Causes
- Injury: Sprains, fractures, or dislocations.
- Overuse Syndromes: Due to repetitive strain on a joint, e.g., tennis elbow.
- Obesity: Excess weight causing stress on weight-bearing joints.
5. Systemic and Metabolic Causes
- Fibromyalgia: Chronic pain disorder affecting joints and muscles.
- Hypothyroidism: May cause generalized joint pain.
- Vitamin D Deficiency: Leads to bone and joint discomfort.
6. Other Causes
- Hormonal Changes: During menopause or pregnancy.
- Stress and Emotional Factors: Can exacerbate perception of pain.
Complications of Untreated Joint Pain
- Chronic disability or reduced mobility.
- Joint deformities.
- Systemic complications (e.g., heart issues in RA).
- Poor quality of life due to persistent pain.
Ayurvedic Perspective on Joint Pain
In Ayurveda, joint pain is often categorized under Sandhi Vata (joint disorders) and is primarily attributed to an imbalance in the Vata dosha (air and space elements). Secondary imbalances of Pitta or Kapha doshas may also be involved.
Types of Joint Pain in Ayurveda
- Vataja Sandhigata Roga: Pain due to aggravated Vata; characterized by stiffness, cracking sounds, and dryness.
- Aamavata (Rheumatoid Arthritis): Caused by Ama (toxins) accumulation due to poor digestion; presents as swelling, stiffness, and fever.
- Vatarakta (Gout): Due to the combined vitiation of Vata and Rakta (blood).
- Sandhigata Kapha: Swelling and heaviness in joints due to Kapha accumulation.
Ayurvedic Treatment for Joint Pain
1. Detoxification (Shodhana Therapy)
- Virechana (Purgation): To remove toxins and balance Pitta.
- Basti (Enema): Medicated oil or herbal decoctions are administered to balance Vata.
2. Oher therapies
- Abhyanga (Oil Massage): Relieves stiffness and nourishes joints. Oils like Mahanarayan Taila or Dhanwantharam Taila are often used.
- Swedana (Fomentation): Herbal steam therapy to reduce stiffness and swelling.
- Janu Basti or Greeva Basti: Localized oil retention therapy for knee or cervical pain.
Internal Medications
- Maha Yogaraj Guggulu: For chronic joint pain.
- Dashmoolarishta: Balances Vata and reduces inflammation.
- Panchatikta Ghrita Guggulu: For detoxification and healing.
Dietary Changes:
- Favour warm, easily digestible foods.
- Include anti-inflammatory spices like turmeric and ginger.
- Avoid cold, raw, and processed foods.
Lifestyle Tips:
- Maintain an active routine with gentle exercises like yoga.
- Avoid cold exposure and overexertion.
- Regular exercise, Yoga and Pranayama
Herbal Remedies
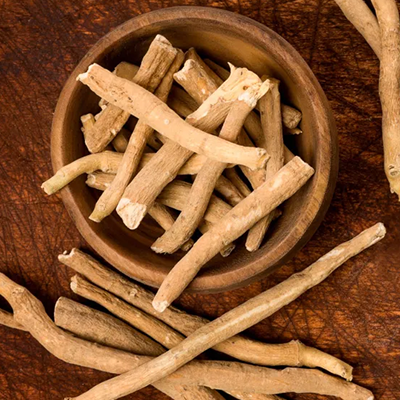
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera):
Anti-inflammatory and rejuvenative.
Shallaki(Boswellia serrata):
Reduces inflammation and joint stiffness.
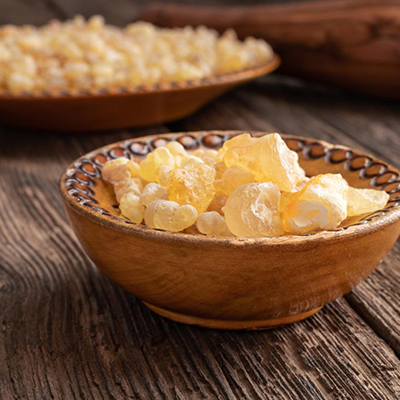
Guggulu (Commiphora mukul):
Effective in reducing joint pain and swelling.
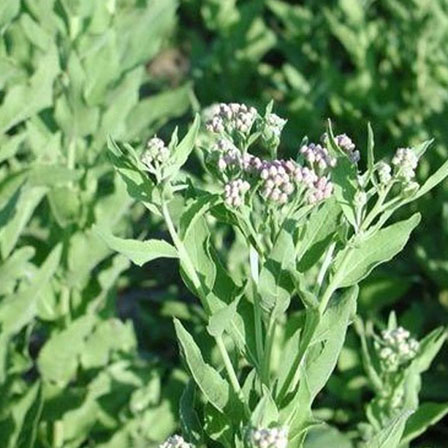
Rasna (Pluchea lanceolata):
Used for musculoskeletal disorders.
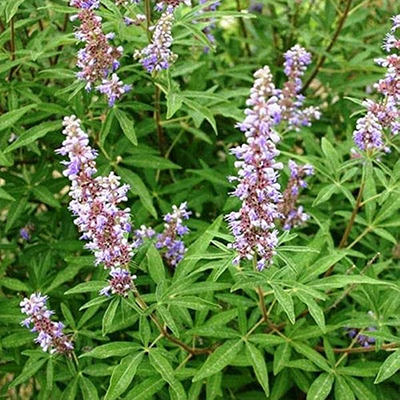
Nirgundi (Vitex negundo):
Relieves pain and reduces swelling.
While modern medicine focuses on diagnosis and symptomatic relief through medications like NSAIDs or DMARDs (for autoimmune conditions), Ayurveda offers a holistic approach to address root causes, enhance immunity, and improve joint health through detoxification and rejuvenation therapies. Combining both can provide comprehensive and sustainable management for joint pain.